Interferon-induced immune signatures are associated with suppression of HEV infection in porcine cell culture models
- PMID: 40576562
- PMCID: PMC12269117
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2025.2525269
Interferon-induced immune signatures are associated with suppression of HEV infection in porcine cell culture models
Abstract
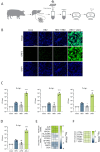
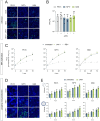
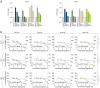
Hepatitis E virus genotype 3 (HEV-3) is a zoonotic pathogen with pigs representing the natural host. Although HEV-3 infections in humans are often self-limiting, severe or chronic cases can occur. In contrast, HEV-3 infections in pigs, the primary reservoir, remain asymptomatic. To assess the initial transcriptional response in porcine cells during HEV-3 infection and pave the way for mechanistic studies of species-specific virus-host interactions, we aimed to establish porcine cell culture models, including primary porcine hepatocytes (PPHs) and porcine cell lines. PPHs supported the full HEV-3 replication cycle while intrinsic immunity, driven by the interferon-stimulated gene (ISG) system, played a central role in restricting viral replication. JAK inhibition enhanced viral replication and suppressed ISG expression, highlighting the importance of IFN signalling in antiviral defense. Transcriptional profiling revealed a global modulation of host responses upon HEV infection, including pathways linked to immunity, inflammation, and metabolism. Porcine cell lines were permissive to HEV infection and treatment with recombinant porcine IFN-α subtypes induced a robust ISG response and effectively inhibited HEV replication in a dose-dependent manner. These findings establish porcine hepatocytes and cell lines as valuable tools to study HEV-host interactions, demonstrating the critical role of IFN-mediated intrinsic immunity in HEV restriction and highlighting subtype-specific antiviral effects of porcine IFN-α.
Keywords: Hepatitis E virus; cell culture models; innate immunity; natural host; pigs; zoonosis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


References
-
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation . (2024). Global burden of disease study 2021 (GBD 2021) burden and strength of evidence by risk factor 1990–2021.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
