Harnessing hybrid perception on multi-scale features for hand-foot-mouth disease multi-region prediction based on Seq2Seq
- PMID: 40577364
- PMCID: PMC12204527
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0326206
Harnessing hybrid perception on multi-scale features for hand-foot-mouth disease multi-region prediction based on Seq2Seq
Abstract
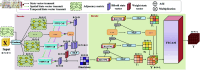
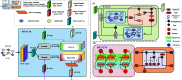
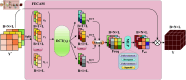
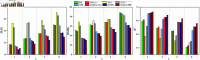
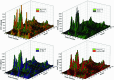
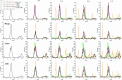
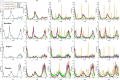
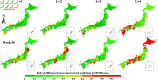
Accurate prediction of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is crucial for effective epidemic prevention and control. Existing prediction models often overlook the cross-regional transmission dynamics of HFMD, limiting their applicability to single regions. Furthermore, their ability to perceive spatio-temporal features holistically remains limited, hindering the precise modeling of epidemic trends. To address these limitations, a novel HFMD prediction model named Seq2Seq-HMF is proposed, which is based on the Sequence-to-Sequence(Seq2Seq) framework. This model leverages hybrid perception of multi-scale features. First, the model utilizes graph structure modeling for multi-regional epidemic-related features. Secondly, a novel Spatio-Temporal Parallel Encoding(STPE) Cell is designed; multiple STPE Cells constitute an encoder capable of hybrid perception across multi-scale spatio-temporal features. Within this encoder, graph-based feature representation and iterative convolution operations enable the capture of cumulative influence of neighboring regions across temporal and spatial dimensions, facilitating efficient extraction of spatio-temporal dependencies between multiple regions. Finally, the decoder incorporates a frequency-enhanced channel attention mechanism(FECAM) to improve the model's comprehension of temporal correlations and periodic features, further refining prediction accuracy and multi-step forecasting capabilities. Experimental results, utilizing multi-regional data from Japan to predict HFMD cases one to four weeks ahead, demonstrate that our proposed Seq2Seq-HMF model outperforms baseline models. Additionally, the model performs well on single-region data from a city in southern China, confirming its strong generalization ability.
Copyright: © 2025 Lei et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Influence of the Enterovirus 71 Vaccine and the COVID-19 Pandemic on Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease in China Based on Counterfactual Models: Observational Study.JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024 Dec 17;10:e63146. doi: 10.2196/63146. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024. PMID: 39692430 Free PMC article.
-
Spatio-temporal transformer and graph convolutional networks based traffic flow prediction.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 7;15(1):24299. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-10287-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40624240 Free PMC article.
-
A PatchTST-GRU based heterogeneous seq2seq model with numerical weather prediction refinement for multi-step wind power forecasting.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 25;15(1):16547. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-00741-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40562840 Free PMC article.
-
Best practices to prevent transmission and control outbreaks of hand, foot, and mouth disease in childcare facilities: a systematic review.Hong Kong Med J. 2017 Apr;23(2):177-90. doi: 10.12809/hkmj166098. Epub 2017 Mar 17. Hong Kong Med J. 2017. PMID: 28302925
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

