Mode of birth and maternal depression/severe anxiety: Findings from Millennium Cohort Study
- PMID: 40577375
- PMCID: PMC12204560
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0327129
Mode of birth and maternal depression/severe anxiety: Findings from Millennium Cohort Study
Abstract
Introduction: Limited evidence exists on the association between mode of birth and long-term depression and/or severe anxiety in mothers. We aimed to examine the association between mode of birth and depression and/or severe anxiety by 14 years postpartum.
Methods: We used data from the Millennium Cohort Study. Data on mode of birth were collected when mothers were 9 months postpartum, and categorized as spontaneous vaginal birth (VB), assisted VB, induced VB, emergency cesarean section (CS), planned CS, and CS after induction. Depression/severe anxiety were collected as one variable and self reported by mothers at 9 months, 3, 5, 7, 11, and 14 years postpartum based on a doctor diagnosis. The primary outcome measure was a diagnosis of depression/severe anxiety up to 14 years postpartum. We used multivariable logistic regression models to estimate crude and adjusted odds ratios (OR) for the association between mode of birth and depression/severe anxiety by 14 years postpartum.
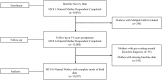
Results: There were 10,507 singleton mothers included in our analyses. Fully adjusted odds ratio (aOR)for the association between mode of birth and depression/severe anxiety by 14 years postpartum was induced VB, (aOR, 1.13 [95% CI], 1.01-2.28), assisted VB (aOR, 1.03 [95% CI], 0.89-1.19), Emergency CS, (aOR, 1.08 [95% CI], 0.92-1.27), planned CS (aOR, 1.09 [95% CI], 0.93-1.27), and CS after induction (aOR, 1.08 [95% CI], 0.91-1.28). Fully adjusted models did not report any significant association between mode of birth and depression/severe anxiety at other postpartum time points.
Conclusions: The present findings provide support for association between induction of labor and the risk of long-term depression/severe anxiety by 14 years postpartum. The findings provide no evidence to support association between other modes of birth and maternal depression/anxiety.
Copyright: © 2025 Bodunde et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
References
-
- Dikete M, Coppieters Y, Trigaux P, Englert Y, Simon P. An analysis of the practices of caesarean section in sub-Saharan Africa: A summary of the literature. Arch Community Med Public Health. 2019;5(2):077–86. doi: 10.17352/2455-5479.000058 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical