Characterization of anti-canine CD20 antibody 4E1-7-B_f and comparison with commercially available anti-human CD20 antibodies
- PMID: 40577406
- PMCID: PMC12204528
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325526
Characterization of anti-canine CD20 antibody 4E1-7-B_f and comparison with commercially available anti-human CD20 antibodies
Abstract
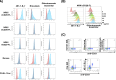
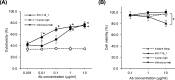
This study characterizes the previously reported anti-canine CD20 antibody 4E1-7-B_f and compares this with commercially available anti-human CD20 antibodies, rituximab and an obinutuzumab biosimilar. While the obinutuzumab biosimilar exhibited binding to canine CD20 in a CD20-transduced cell line, canine B-cell lymphoma cell line (CLBL-1/luc), and canine CD21 + B cells from healthy dogs, functional assays revealed the superiority of 4E1-7-B_f in antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and complement-dependent cytotoxicity activities over those of the obinutuzumab biosimilar. Epitope analysis suggested an extracellular region on canine CD20 targeted by 4E1-7-B_f. Furthermore, the lipid raft localization of CD20 in CLBL-1/luc cells by treatment with 4E1-7-B_f classified this antibody as a type II anti-CD20 antibody which works with strong ADCC activity, similar to the obinutuzumab biosimilar, unlike rituximab, a type I anti-CD20 antibody, whose main action is CDC activity. These findings underscore the potential clinical utility of 4E1-7-B_f, emphasizing the specificity, potency, and therapeutic promise in canine lymphoma treatment.
Copyright: © 2025 Mizuno et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have read the journal’s policy and have the following competing interests: TT is an employee of Nippon Zenyaku Kogyo Co., Ltd. There are no patents, products in development or marketed products associated with this research to declare. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Generation of a canine anti-canine CD20 antibody for canine lymphoma treatment.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 10;10(1):11476. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68470-9. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32651429 Free PMC article.
-
B cell-extrinsic and intrinsic factors linked to early immune repletion after anti-CD20 therapy in patients with multiple sclerosis of African ancestry.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 10;16:1590165. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1590165. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40557147 Free PMC article.
-
A bispecific antibody directly induces lymphoma cell death by simultaneously targeting CD20 and HLA-DR.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015 Nov;141(11):1899-907. doi: 10.1007/s00432-015-1949-7. Epub 2015 Mar 14. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25773122 Free PMC article.
-
Rituximab, ofatumumab and other monoclonal anti-CD20 antibodies for chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Nov 14;11(11):CD008079. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008079.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23152253 Free PMC article.
-
Late-onset neutropenia after rituximab treatment: case series and comprehensive review of the literature.Medicine (Baltimore). 2010 Sep;89(5):308-318. doi: 10.1097/MD.0b013e3181f2caef. Medicine (Baltimore). 2010. PMID: 20827108
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

