Functional analysis of CYP4B1 enzymes from apes and humans uncovers evolutionary hot spots for adaptations of the catalytical function
- PMID: 40577420
- PMCID: PMC12233900
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011750
Functional analysis of CYP4B1 enzymes from apes and humans uncovers evolutionary hot spots for adaptations of the catalytical function
Abstract
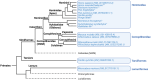
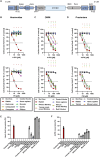
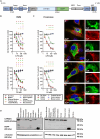
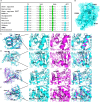
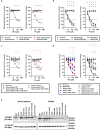
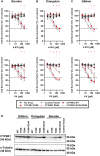
A hallmark of the highly conserved CYP4B1 enzyme in mammals is the capability to bioactivate both xenobiotic and endobiotic substrates. However, due to a single amino acid change (p.P427S) within the evolutionary conserved meander region no catalytic activity of the native human CYP4B1 has been identified so far. To identify at which point in human evolution the loss of CYP4B1 activity had occurred, we evaluated the activities of CYP4B1 orthologs from 14 primate genera against 4-ipomeanol and perilla ketone in human liver cells. The activity of recombinant CYP4B1 proteins isolated from E. coli was also tested against 4-ipomeanol and lauric acid. Surprisingly, CYP4B1 already became catalytically inactive at the split between apes and monkeys; all tested CYP4B1 orthologs from monkeys were able to bioactivate both protoxins and to hydroxylate lauric acid. Amino acid analysis of the CYP4B1 orthologs revealed four additional evolutionary changes, each affecting the function of ape and human enzymes: p.V71G specific for Denisovans, p.R106C, p.R244H, and an exon deletion found only in the gorilla CYP4B1. Systematic functional analyses proved the negative impact of the genetic changes on CYP4B1 activity and showed that reversion of the mutations restored enzyme activity. The occurrence of five independent inactivating genetic changes in the same gene of closely related species is a clear indication of the importance of inactivating CYP4B1 in apes and humans. Elucidating the evolutionary trigger(s) for CYP4B1 inactivation in our ancestors will ultimately improve our understanding of primate evolution.
Copyright: © 2025 Hüsken et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dasgupta A. Chapter 4 - Genetic Factors Associated With Opioid Therapy and Opioid Addiction. In: Dasgupta A, editor. Fighting the Opioid Epidemic. Elsevier. 2020. p. 61–88.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

