Global health risks lurking in livestock resistome
- PMID: 40577477
- PMCID: PMC12204175
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adt8073
Global health risks lurking in livestock resistome
Abstract
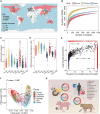
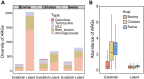
Livestock farming consumes more than 70% of global antibiotics annually, making livestock manures an important vector of anthropogenically influenced antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs). The global pattern of the livestock resistome, its driving mechanisms, and transmission potential to the clinic are not well assessed. We analyzed 4017 livestock manure metagenomes from 26 countries and constructed a comprehensive catalog of livestock ARGs and metagenome-assembled genomes. Livestock resistome is a substantial reservoir of known (2291 subtypes) and latent ARGs (3166 subtypes) and is highly connectable to human resistomes. We depicted the global pattern of livestock resistome and prevalence of clinically critical ARGs, highlighting the role of farm and human antibiotic stewardship in shaping livestock resistome. We developed a risk-assessment framework by integrating mobility potential, clinical significance, and host pathogenic relevance, and prioritized higher risk livestock ARGs, producing a predictive global map of livestock resistome risks that can help guide research and policy.
Figures




References
-
- Van Boeckel T. P., Pires J., Silvester R., Zhao C., Song J., Criscuolo N. G., Gilbert M., Bonhoeffer S., Laxminarayan R., Global trends in antimicrobial resistance in animals in low- and middle-income countries. Science 365, eaaw1944 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

