Substantial Hierarchical Reductions of Genetic and Morphological Traits in the Evolution of Rotiferan Parasites
- PMID: 40577491
- PMCID: PMC12256650
- DOI: 10.1093/gbe/evaf124
Substantial Hierarchical Reductions of Genetic and Morphological Traits in the Evolution of Rotiferan Parasites
Abstract
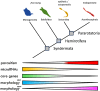
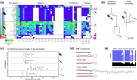
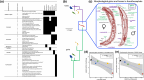
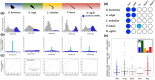
Within the last 800 million years, animals evolved a vast range of diversity of species exhibiting an enormous disparity of forms and lifestyles. The process involved an increase in complexity from life forms with few cell types to organisms with many hundreds of cell types. However, neither genome size nor number of protein-coding genes can explain these differences, and their biological basis remains elusive. Yet, recent studies suggest that the evolution of complexity is closely linked to the acquisition of a class of noncoding gene regulators called microRNAs. To test this hypothesis, we investigated the association between loss of organismal complexity and microRNAs in Syndermata, an invertebrate group including free-living wheel animals (Monogononta, Bdelloidea), epibiotic Seisonidea, and endoparasitic thorny-headed worms (Acanthocephala). Analyses of genomic, transcriptomic, and morphological data of altogether 25 syndermatan species revealed strong correlations of microRNA losses with reductions of protein-coding genes and morphological traits. The hierarchical pattern sums up to ∼85% loss of microRNAs and a ∼50% loss of conserved metazoan core genes (Benchmarking Universal Single-Copy Orthologs) on the lineage to thorny-headed worms. Extraordinarily reduced microRNA complements were confirmed by small RNA sequencing data. Endoparasitic Acanthocephala was additionally distinguished by the most morphological reductions of ancestral features, such as the digestive tract. Together, we observed that reductions of ∼400 protein-coding genes and 10 metazoan core genes tended to accompany the loss of single microRNA families. Furthermore, 4 microRNA families and 34 metazoan core genes appeared to be associated, on average, with the reduction of a single morphological trait.
Keywords: Rotifera; complexity; core genes; evolution; microRNAs; piRNAs.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Society for Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Figures


References
-
- Ahlrichs W. Ultrastruktur und Phylogenie von Seison nebaliae (Grube 1859) und Seison annulatus (Claus 1876): Hypothesen zu phylogenetischen Verwandtschaftsverhältnissen innerhalb der Bilateria. Göttingen, Germany: Cuvillier; 1995.
-
- Ahlrichs WH. Epidermal ultrastructure of Seison nebaliae and Seison annulatus, and a comparison of epidermal structures within the Gnathifera. Zoomorphology. 1997:117(1):41–48. 10.1007/s004350050028. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

