Reference-based chromosome-scale assembly of Japanese barley (Hordeum vulgare ssp. vulgare) cultivar Hayakiso 2
- PMID: 40577690
- PMCID: PMC12232906
- DOI: 10.1093/dnares/dsaf016
Reference-based chromosome-scale assembly of Japanese barley (Hordeum vulgare ssp. vulgare) cultivar Hayakiso 2
Abstract
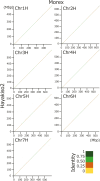
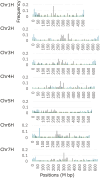
Current advances in next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology and assembling programs permit construct chromosome-level genome assemblies in various plants. In contrast to resequencing, the genome sequences provide comprehensive annotation data useful for plant genetics and breeding. Herein, we constructed a reference-based genome assembly of winter barley (H. vulgare ssp. vulgare) cv. 'Hayakiso 2' using long and short read NGS data and barley reference genome sequences from 'Morex'. We constructed 'Hayakiso 2' genome sequences covering 4.3 Gbp with 55,477 genes. Comparative genomics revealed that 14,106 genes had orthologs to two barley data, wheat (A, B, and D homoeologs, respectively), and rice. From the gene ontology analysis, 2,494 orthologs against wheat and rice but not two barley contained agricultural important genes, such as 'response to biotic and abiotic stress' and 'metabolic process'. Phylogenetic analysis using 76 pangenome data indicated that 'Hayakiso 2' was clustered into Japanese-type genomes with unique alleles. 'Hayakiso 2' genome sequences showed known genes related to flowering and facilitated barley breeding through the development of various markers related to agronomically important alleles such as tolerance to various types of biotic and abiotic stress. Therefore, 'Hayakiso 2' genome sequences will be used for the further barley breeding.
Keywords: Hordeum vulgare; genome sequencing; long-read sequencing.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Kazusa DNA Research Institute.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the HvGATA gene family under abiotic stresses in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.).BMC Genomics. 2025 Jul 7;26(1):637. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11834-0. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40619360 Free PMC article.
-
Genome resequencing and transcriptome profiling reveal molecular evidence of tolerance to water deficit in barley.J Adv Res. 2023 Jul;49:31-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2022.09.008. Epub 2022 Sep 25. J Adv Res. 2023. PMID: 36170948 Free PMC article.
-
A pangenome reference of wild and cultivated rice.Nature. 2025 Jun;642(8068):662-671. doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-08883-6. Epub 2025 Apr 16. Nature. 2025. PMID: 40240605 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic test accuracy and cost-effectiveness of tests for codeletion of chromosomal arms 1p and 19q in people with glioma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Mar 2;3(3):CD013387. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013387.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35233774 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sasaki T, International Rice Genome Sequencing Project (IRGSP). The map-based sequence of the rice genome. Nature. 2005:436:793–800. - PubMed
-
- Ichihara H, et al. Plant GARDEN: a portal website for cross-searching between different types of genomic and genetic resources in a wide variety of plant species. BMC Plant Biol. 2023:23:391. https://doi.org/ 10.1186/s12870-023-04392-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jayakodi M, et al. Structural variation in the pangenome of wild and domesticated barley. Nature. 2024:636:654–662. https://doi.org/ 10.1038/s41586-024-08187-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Walkowiak S, et al. Multiple wheat genomes reveal global variation in modern breeding. Nature. 2020:588:277–283. https://doi.org/ 10.1038/s41586-020-2961-x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shirasawa K, et al. Chromosome-scale genome assembly of Eustoma grandiflorum, the first complete genome sequence in the genus Eustoma,. G3 (Bethesda, Md.). 2023:13:jkac329. https://doi.org/ 10.1093/g3journal/jkac329 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

