Targeting the CD40 costimulatory receptor to improve virotherapy efficacy in diffuse midline gliomas
- PMID: 40578365
- PMCID: PMC12281365
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102204
Targeting the CD40 costimulatory receptor to improve virotherapy efficacy in diffuse midline gliomas
Abstract
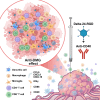
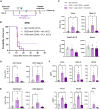
Diffuse midline glioma (DMG) is a devastating pediatric brain tumor. The oncolytic adenovirus Delta-24-RGD has shown promising efficacy and safety in DMG patients but is not yet curative. Thus, we hypothesized that activating dendritic cells (DCs) through the CD40 costimulatory receptor could increase antigen presentation and enhance the anti-tumor effect of the virus, resulting in long-term responses. This study shows that the intratumoral co-administration of Delta-24-RGD and a CD40 agonistic antibody is well tolerated and induces long-term anti-tumor immunity, including complete responses (up to 40%) in DMG preclinical models. Mechanistic studies revealed that this therapy increased tumor-proliferating T lymphocytes and proinflammatory myeloid cells, including mature DCs with superior tumor antigen uptake capacity. Moreover, the lack of cross-presenting DCs and the prevention of DC recruitment into the tumor abolish the Delta-24-RGD+anti-CD40 anti-DMG effect. This approach shows potential for combining virotherapy with activating antigen-presenting cells in these challenging tumors.
Keywords: CD40; DIPG; DMG; Delta-24-RGD; dendritic cells; diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma; diffuse midline glioma; oncolytic adenovirus.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests M.M.A. and J.G.P.-L. have a patent application PCT/US2022/026392 (Use of oncolytic adenovirus for the treatment of pediatric brain cancer) filed by the host institution and DNAtrix on April 26, 2022 (currently in prosecution in Europe and the USA).
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

