Prevalence of low-level viremia in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40578863
- PMCID: PMC12207133
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-088756
Prevalence of low-level viremia in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: Low-level viremia (LLV) is a risk factor affecting the prognosis of patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB). The objective of this study was to systematically assess the prevalence of LLV, thereby providing robust evidence-based medical insights into effective clinical interventions and preventative measures against LLV.
Design: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
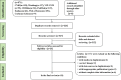
Data sources: A comprehensive literature search was conducted across various databases, including China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Wanfang Data (Wanfang), China Science And Technology Journal Database (VIP-CSTJ), China Biology Medicine disc (CBMdisc), PubMed, Embase, Web of Science and the Cochrane Library, spanning from the inception of these databases up to 5 January 2024.
Eligibility criteria: The research type included either a cross-sectional study or a cohort study focusing on the Chinese population, with the outcome being LLV. The languages were limited to both Chinese and English. Studies with any of the following were excluded: subjects with other comorbidities, original articles inaccessible or data unavailable, and duplicate publications.
Data extraction and synthesis: Literature management used EndNote X9.1, and an information extraction table was created using Microsoft Excel to record research information, including first author, year of publication and study type. The prevalence of LLV was assessed via meta-analysis. Meta-analyses were conducted in RStudio using the 'metaprop ()' function. Subgroup analysis and sensitivity analysis were used to identify sources of heterogeneity, and funnel plots and AS-Thompson tests were employed to evaluate publication bias.
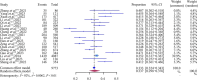
Results: 18 studies, encompassing a total sample of 9773 patients, were included in the analysis. Of these, 3336 patients were identified with LLV. The meta-analysis revealed that the prevalence of LLV among treated CHB patients stands at 33.6% (95% CI 30.2 to 37.0). The antigen status, antiviral treatment regimen (type of drugs and nucleos(t)ide analogues (NAs)), treatment duration, medication adherence and baseline hepatitis B virus DNA levels all affected the prevalence of LLV. Sensitivity analysis further corroborated the stability of these meta-analysis findings. The funnel plot and AS-Thompson test indicated no significant publication bias (t = -0.01, p=0.995).
Conclusions: The prevalence of LLV among CHB patients was established at 33.7% (95% CI 29.8% to 37.6%). Thus, it is imperative for clinical decision-makers to consider the various influencing factors of LLV when formulating treatment plans in order to mitigate any potential adverse outcomes.
Keywords: China; Hepatology; INFECTIOUS DISEASES; Meta-Analysis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
-
Direct-acting antivirals for chronic hepatitis C.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 6;6(6):CD012143. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012143.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 18;9:CD012143. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012143.pub3. PMID: 28585310 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Direct-acting antivirals for chronic hepatitis C.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 18;9(9):CD012143. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012143.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28922704 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- World Health Organization(WHO) . Hepatitis B.Fact sheets.(2024-4-9)[2024-10-29].
-
- Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association . Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B (2022 version). Chin J Hepatol 2023;41:3–28. 10.3760/cma.j.cn311365-20230220-00050 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials