Dysregulated Pro-inflammatory and Anti-inflammatory Cytokine Responses to Microbe-associated Molecular Patterns in X-linked Chronic Granulomatous Disease
- PMID: 40578979
- PMCID: PMC12223621
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.13989
Dysregulated Pro-inflammatory and Anti-inflammatory Cytokine Responses to Microbe-associated Molecular Patterns in X-linked Chronic Granulomatous Disease
Abstract
Background/aim: Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) is a hereditary immune deficiency caused by mutations in nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase subunits. X-linked CGD caused by mutations in gp91phox is characterized by recurrent bacterial and fungal infections and by an increased incidence of autoimmunity and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The concurrent occurrence of microbial infection, autoimmunity, and IBD suggests the presence of complicated profiles of cytokines in patients with CGD. However, the pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine responses to microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs) are poorly defined in patients with CGD.
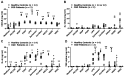
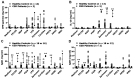
Patients and methods: We evaluated the cytokine and chemokine profiles in two patients with X-linked CGD. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated and stimulated with various bacterial and fungal MAMPs.
Results: Production of C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 8, interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-10, and tumor necrosis factor-α was enhanced by PBMCs isolated from patients with X-linked CGD as compared with those from healthy controls when stimulated with bacterial and fungal MAMPs.
Conclusion: A dysregulated balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines may contribute to the manifestations of recurrent infection, autoimmunity, and IBD in patients with X-linked CGD.
Keywords: Microbe-associated molecular patterns; chronic granulomatous disease; cytokines.
Copyright © 2025, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this study.
Figures
References
-
- Roos D, de Boer M, Kuribayashi F, Meischl C, Weening RS, Segal AW, Ahlin A, Nemet K, Hossle JP, Bernatowska-Matuszkiewicz E, Middleton-Price H. Mutations in the x-linked and autosomal recessive forms of chronic granulomatous disease. Blood. 1996;87(5):1663–1681. - PubMed
-
- Marciano BE, Spalding C, Fitzgerald A, Mann D, Brown T, Osgood S, Yockey L, Darnell DN, Barnhart L, Daub J, Boris L, Rump AP, Anderson VL, Haney C, Kuhns DB, Rosenzweig SD, Kelly C, Zelazny A, Mason T, DeRavin SS, Kang E, Gallin JI, Malech HL, Olivier KN, Uzel G, Freeman AF, Heller T, Zerbe CS, Holland SM. Common severe infections in chronic granulomatous disease. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;60(8):1176–1183. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu1154. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kuhns DB, Alvord WG, Heller T, Feld JJ, Pike KM, Marciano BE, Uzel G, DeRavin SS, Priel DA, Soule BP, Zarember KA, Malech HL, Holland SM, Gallin JI. Residual NADPH oxidase and survival in chronic granulomatous disease. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(27):2600–2610. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1007097. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
