Embolic Stroke Due to a Large Noncoronary Sinus of Valsalva Aneurysm: A Multimodality Imaging Diagnosis
- PMID: 40579110
- PMCID: PMC12273851
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2025.103761
Embolic Stroke Due to a Large Noncoronary Sinus of Valsalva Aneurysm: A Multimodality Imaging Diagnosis
Abstract
Background: A sinus of Valsalva aneurysm (SoVA) is a rare cardiac condition caused by the dilation of a coronary sinus. If untreated, it can commonly lead to valvular dysfunction, arrhythmias, or rupture.
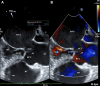
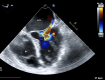
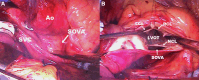
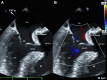
Case summary: A 71-year-old patient with hypertension and hyperlipidemia presented with an embolic stroke. Multimodality imaging revealed a large, 7.0 cm × 5.6 cm SoVA originating from the noncoronary sinus and causing nearly complete obstruction of the left atrium. The aneurysm was surgically repaired, and the patient made a full recovery.
Discussion: In rare cases, a stroke may be the initial presentation of a SoVA. The probable cause of the patient's stroke was attributed to thrombus formation within the SoVA that embolized.
Take-home messages: This case emphasizes the importance of multimodality imaging for the diagnosis of a SoVA and for planning surgical repair. Additionally, clinicians should consider a SoVA in the differential diagnosis for a patient presenting with a stroke.
Keywords: aortic root repair; computed tomography; coronary angiography; multimodality cardiac imaging; noncoronary sinus; sinus of Valsalva aneurysm; stroke; transesophageal echocardiogram; transthoracic echocardiogram.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding Support and Author Disclosures The authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures




References
-
- Takach T.J., Reul G.J., Duncan J.M., et al. Sinus of Valsalva aneurysm or fistula: management and outcome. Ann Thorac Surg. 1999;68(5):1573–1577. - PubMed
-
- Dev V., Goswami K.C., Shrivastava S., et al. Echocardiographic diagnosis of aneurysm of the sinus of Valsalva. Am Heart J. 1993;126:930–936. - PubMed
-
- Feldman D.N., Roman M.J. Aneurysms of the sinuses of Valsalva. Cardiology. 2006;106:73–81. - PubMed
-
- Fishbein M.C., Obma R., Roberts W.C. Unruptured sinus of Valsalva aneurysm. Am J Cardiol. 1975;35:918–922. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

