Nanopore detection of single-nucleotide RNA mutations and modifications with programmable nanolatches
- PMID: 40579472
- PMCID: PMC12534182
- DOI: 10.1038/s41565-025-01965-6
Nanopore detection of single-nucleotide RNA mutations and modifications with programmable nanolatches
Abstract
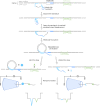
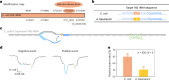
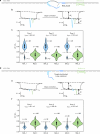
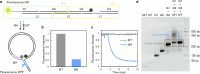
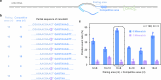
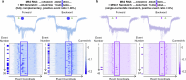
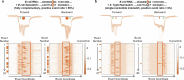
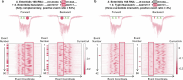
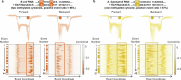
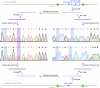
RNA mutations and modifications have been implicated in a wide range of pathophysiologies. However, current RNA detection methods are hindered by data complexity and error-prone protocols, restricting their widespread use. Here we present a solid-state nanopore-based approach, RNA single-nucleotide characterization and analysis nanolatch (RNA-SCAN) system, which simplifies the detection of nucleotide mutations and modifications in RNA with high resolution. Using phage RNA as a template, we tested multiple sequences and chemical modifications on nanolatches, allowing the detection of mismatches caused by nucleotide mutations through significant changes in positive event ratios using single-molecule nanopore measurements. This approach is also sensitive to modifications that either strengthen or weaken the interaction between the target RNA sequence and the nanolatch. As a proof-of-concept, we demonstrate successful discrimination of Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. from total RNA based on nucleotide variations in their 16S rRNA, as well as quantification of different Salmonella spp. and detection of m5C1407 modification on E. coli 16S rRNA. The RNA-SCAN approach demonstrates the feasibility of combining RNA/DNA hybrid nanotechnology with nanopore sensing and diagnosing RNA-related health conditions.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Chatterjee, A., Mambo, E. & Sidransky, D. Mitochondrial DNA mutations in human cancer. Oncogene25, 4663–4674 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Goodall, G. J. & Wickramasinghe, V. O. RNA in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer21, 22–36 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Barbieri, I. & Kouzarides, T. Role of RNA modifications in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer20, 303–322 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2023JJ12SN032/Dalian University of Technology (DUT)
- 62471081/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 215515/Z/19/Z/Wellcome Trust (Wellcome)
- 964995/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

