Defactinib with avutometinib in patients with solid tumors: the phase 1 FRAME trial
- PMID: 40579546
- PMCID: PMC12443583
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-025-03763-y
Defactinib with avutometinib in patients with solid tumors: the phase 1 FRAME trial
Abstract
Use of signal transduction inhibitors as single agents to treat cancer leads to resistance because of the plasticity of intracellular signaling, and combination therapy can overcome this. We describe the first-in-human trial of avutometinib (RAF-MEK clamp) and defactinib (focal adhesion kinase inhibitor) in patients with solid tumors. The trial met its primary endpoint and recommended a phase 2 dose and schedule. The recommended phase 2 dose and schedule for a 28-day cycle was determined to be avutometinib 3.2 mg once a day, twice weekly (Monday and Thursday or Tuesday and Friday), and defactinib 200 mg twice a day, seven days a week. Both drugs were administered orally on a 3 weeks 'on' and 1 week 'off' basis. The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics were consistent with previous reports of avutometinib and defactinib used as single agents. Key findings include an objective response rate of 42.3% (11 of 26; 95% confidence interval 23.4-63.1) and a median progression-free survival of 20.1 months (95% confidence interval 11.2-43.9) in patients with low-grade serous ovarian cancer. This study demonstrates the importance of intermittent dosing schedules in combined targeting of the mitogen-activated protein kinase and focal adhesion kinase pathways to improve tolerability, and has acquired proof of concept of anti-tumor activity against low-grade serous ovarian cancer, a tumor relatively resistant to chemotherapy. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT03875820 .
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: S.B. has received honoraria for consulting and/or advisory board work from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BioNTech, Eisai, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Grey Wolf Therapeutics, Immunogen, Incyte, ITM Oncologics, Lilly, Merck Sharpe Dohme, Mersana, Myriad, Oncxerna, Pharmaand, Seagen, TORL BioTherapeutics, Verastem, Zymeworks; honoraria and/or expenses from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Immunogen, Merck Sharpe Dohme, Mersana, Takeda, Verastem and Zymeworks; research funding from AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline; and PI for Global/ENGOT lead RAMP201 and ENGOT lead RAMP301 (Verastem-sponsored). M.G.K. has a consulting or advisory role with Bayer, Guardant Health, Janssen, Roche, Seattle Genetics and Zai Lab; has received speaker fees from BMS, Eisai, Janssen, Roche and Servier; travel, accommodation or expenses from BerGenBio, BMS, Janssen, Roche, Servier and Zai Lab; and research grants from Novartis and Roche. A.G. declares no competing interests. A.I.G. declares no competing interests. V.S.P. declares no competing interests. A.T. declares no competing interests. R.S. has received travel expenses from Bayer and for educational symposia from AstraZeneca. R.C. declares no competing interests. R.G. declares no competing interests. M.R. is an Institute for Cancer Research (ICR) employee. R.R. is an ICR employee. R.G. is an ICR employee. K.S. is an ICR employee. N.T. declares no competing interests. T.P. is an ICR employee. M.P. is an ICR employee. S.S. has received research grants from Verastem Oncology, Merck Sharpe Dohme; advisory board honoraria from Ellipses Pharma and Exscientia/Recursion; and is on the nonremunerated advisory board of Duke Street Bio, Ellipsis, Grey Wolf Therapeutics, Merck Sharp and Dohme and Roche. J.R. has received an advisory board honorarium from Novartis and is an ICR employee. C.Y. is an ICR employee and has received honoraria Faron Pharon Pharmaceuticals, Bayer, Trogenix and Merck. A.S. is an ICR employee; has received travel support from Sanofi, Roche-Genentech and Nurix; honoraria as a speaker from Astellas Pharma and Merck Sharp Dohme; and is on the advisory board of DE Shaw Research, CHARM therapeutics, Ellipses Pharma and Droia Ventures. A.P. declares no competing interests. J.L. has received research grants from Roche-Genentech, Astex, Merck Sharp Dohme, Janssen and Verastem Oncology; and is on the advisory boards of Basilia, Roche, GlaxoSmithKline and Servier. A.M. has received research grants Astex, Merck and Merck Sharp Dohme; honoraria from Chugai, Faron, Merck, GlaxoSmithKline, Seagen, Takeda and Janssen; travel support from Amgen and Janssen; and is on the advisory boards of Imugene, Jansson, Merck, Takeda, Merck Sharp Dohme, Genmab, Pfizer, AstraZeneca and Immutep. J.S.d.B. is an ICR employee, named as an inventor, with no financial interest for patent 8,822,438, submitted by Janssen that covers the use of abiraterone acetate with corticosteroids; has received research support from AstraZeneca, Cellcentric, Crescendo, Daiichi, Immunic Therapeutics, MetaCurUm, Myricx, Nurix, Oncternal, Orion and Sanofi Aventis; honoraria from advisory boards of AbbVie, Acai Therapeutics, Amgen, Amunix, Astellas, Bayer, Bioxcel Therapeutics, Celcuity, Crescendo, Daiichi, Dark Blue Therapeutics, Duke Street Bio, Dunad Therapeutics, Endeavor Biomedicines INC, Genentech-Roche, GSK, Macrogenics, Merck Serono, MetaCurUm, Moma Therapeutics, Myricx, Novartis, Nurix, Nuvation Bio, One-Carbon Therapeutics, Oncternal, Orion, Page Therapeutics, Peptone, Pfizer, Takeda, Tango Therapeutics, Tubulis, GmbH and VIR Biotechnology. U.B. is an ICR employee, named as an inventor on patents arising from this trial, ICR has has entered into a license agreement with Verastem Oncology and UB is due to receive a proportion of income arising from this license in accordance with the institute's rewards to discoverers policy; has received research grants from Verastem Oncology, Chugai and Avacta; and honoraria for advisory board work from Carrick Therapeutics, Pharmenable, Ellipses, Amalus Therapeutics, Dania Therapeutics and Pegascy. The Institute of Cancer Research has commercial interests in CYP17, AKT, CHK1, RAF, MPS1, FLT3/Aurora Kinase inhibitors, GCN2 activators, molecular glues and folate targeted thymidylate synthetase inhibitors.
Figures
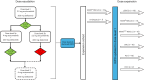
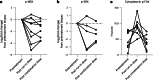

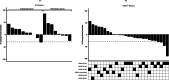

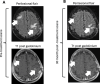
References
-
- Robert, C. et al. Improved overall survival in melanoma with combined dabrafenib and trametinib. N. Engl. J. Med.372, 30–39 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Larkin, J. et al. Combined vemurafenib and cobimetinib in BRAF-mutated melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med.371, 1867–1876 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Kopetz, S. et al. Encorafenib, binimetinib, and cetuximab in BRAF V600E-mutated colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med.381, 1632–1643 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

