Sex Ratio at Birth in Northern Ireland During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Comparison With Published Data From the Republic of Ireland, England and Wales
- PMID: 40579861
- PMCID: PMC12205282
- DOI: 10.1002/ajhb.70099
Sex Ratio at Birth in Northern Ireland During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Comparison With Published Data From the Republic of Ireland, England and Wales
Abstract
Objectives: The COVID-19 pandemic has been linked in several countries to fluctuations in the proportion of male live births/total live births, known as the sex ratio at birth (SRB). This study investigates how the pandemic influenced SRB patterns in Northern Ireland compared to published data from neighboring regions, including the Republic of Ireland with which it shares an open land border, and England and Wales, across the sea.
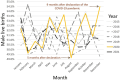
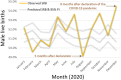
Methods: Monthly live birth data for Northern Ireland from 2015 to 2021 were obtained from the Northern Ireland Statistics and Research Agency. A time series analysis predicted the SRB for 2020 using data from 2015 to 2019. Predicted and observed SRB values were compared for 2020.
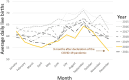
Results: In August 2020, 5 months after the pandemic declaration, the SRB fell significantly to 49.13%, the period's lowest, below the 95% prediction interval (50.09%-51.85%). In December 2020, 9 months after the declaration, the SRB rose to 54.48%, exceeding the prediction interval (49.75%-51.57%). This overall SRB pattern resembled that in England and Wales but differed from the Republic of Ireland.
Conclusion: The decline in SRB in August 2020, occurring 3-5 months after the pandemic declaration, suggests the pandemic disproportionately affected male fetuses in Northern Ireland. The rise in December, 9 months after the declaration, may relate to increased sexual activity in March 2020 following lockdown in a subset of the population. Northern Ireland's SRB pattern aligns more with England and Wales than the Republic of Ireland, indicating that socio-political ties in the United Kingdom may be more influential for pandemic response than geographical proximity.
Keywords: COVID‐19 pandemic; Northern Ireland; male births; sex ratio; stress.
© 2025 The Author(s). American Journal of Human Biology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Rapid, point-of-care antigen tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 22;7(7):CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35866452 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody tests for identification of current and past infection with SARS-CoV-2.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 17;11(11):CD013652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013652.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36394900 Free PMC article.
-
Measures implemented in the school setting to contain the COVID-19 pandemic.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jan 17;1(1):CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 May 2;5:CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029.pub2. PMID: 35037252 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Antibiotic Prescribing by Dental Practitioners Across the United Kingdom's Four Countries: A Pharmacoepidemiological Study of Population-Level Dispensing Data, 2016-2023.Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2025 Aug;53(4):354-361. doi: 10.1111/cdoe.13037. Epub 2025 Mar 10. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2025. PMID: 40064619 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Box, G. E. P. , and Tiao G. C.. 1975. “Intervention Analysis With Applications to Economic and Environmental Problems.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 70, no. 349: 70–79. 10.1080/01621459.1975.10480264. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

