Beyond gold: the chemoenhancing mechanism and therapeutic potential of auranofin in melanoma
- PMID: 40579895
- PMCID: PMC12240195
- DOI: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2025.0026
Beyond gold: the chemoenhancing mechanism and therapeutic potential of auranofin in melanoma
Abstract
Objective: The objective of the current study was to evaluate the chemosensitizing capacity of auranofin (AF), a gold (I) complex traditionally used in rheumatoid arthritis treatment, in potentiating the cytotoxic effects of doxorubicin (DOX) in melanoma cell models, specifically drug-sensitive (B16F10) and multidrug-resistant (B16F10/ADR) variants.
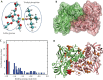
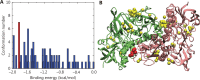
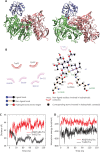
Methods: Experimental measurements, including in vitro cytotoxicity and apoptosis assays, surface plasmon resonance (SPR), immunoblotting assays, as well as theoretical calculations, such as molecular docking and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, were used to systematically delineate the interaction dynamics between AF and thioredoxin reductase 1 (TrxR1). The anti-tumor efficacy of co-treatment with AF and DOX was assessed by examining cell viability and apoptotic rates.
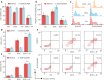
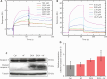
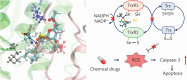
Results: Co-treatment with AF and DOX significantly increased anti-tumor efficacy, as evidenced by reduced cell viability and increased apoptotic rates. This synergistic effect was attributed to inhibition of TrxR1 by AF, which compromised tumor cell antioxidant defenses and elevated intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby enhancing apoptotic pathways. Notably, AF treatment mitigated the heightened TrxR activity in DOX-resistant cells, intensifying the pro-oxidant effects of DOX, leading to increased ROS production and cell death. The data also showed that AF binds with high affinity to the selenocysteine residue within the catalytic site of TrxR1, which partially overlapped with the binding site of the endogenous substrate, thioredoxin (Trx), but with greater avidity. This unique binding configuration impedes the reduction of Trx by TrxR1, triggering an apoptotic response in cancer cells.
Conclusions: This study underscores the chemosensitizing potential of AF in overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer therapy through redox modulation. The molecular mechanism of action underlying AF on TrxR1 demonstrated the unique binding configuration that impedes the reduction of Trx by TrxR1 and instigates an apoptotic response in cancer cells. These findings pave the way for the clinical application of AF as a chemosensitizer, offering a novel approach to augment the efficacy of existing chemotherapy regimens.
Keywords: Auranofin; TrxR1; anti-cancer; drug resistance; molecular dynamics simulation.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest are disclosed.
Figures




References
-
- Freyberg RH, Block WD, Levey S. Metabolism, toxicity and manner of action of gold compounds used in the treatment of arthritis. I. Human plasma and synovial fluid concentration and urinary excretion of gold during and following treatment with gold sodium thiomalate, gold sodium thiosulfate, and colloidal gold sulfide. J Clin Invest. 1941;20:401–12. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Giannini EH, Brewer EJ, Jr, Person DA. Auranofin in the treatment of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Pediatr. 1983;102:138–41. - PubMed
-
- Muranaka M, Miyamoto T, Shida T, Kabe J, Makino S, Okumura H, et al. Gold salt in the treatment of bronchial asthma--a double-blind study. Ann Allergy. 1978;40:132–7. - PubMed
-
- Navarro M, Pérez H, Sánchez-Delgado RA. Toward a novel metal-based chemotherapy against tropical diseases. 3. Synthesis and antimalarial activity in vitro and in vivo of the new gold-chloroquine complex (Au(PPh3)(CQ))PF6. J Med Chem. 1997;40:1937–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
