Emerging concepts and challenges in the development of disease-modifying osteoarthritis drugs - a more refined perspective
- PMID: 40580372
- PMCID: PMC12241195
- DOI: 10.1007/s12272-025-01551-3
Emerging concepts and challenges in the development of disease-modifying osteoarthritis drugs - a more refined perspective
Abstract
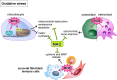
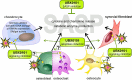
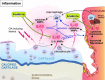
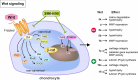
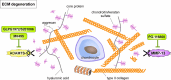
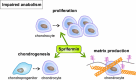
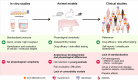
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common joint disease worldwide. Despite significant efforts byresearchers, no disease-modifying osteoarthritis drugs (DMOADs) have been approved yet. This review compares preclinical and clinical studies of promising therapeutic approaches to gain insights into the potential reasons for their failure in clinical trials. For this purpose, prime examples of different therapeutic groups, including the antioxidant NAC, senotherapeutic UBX0101, anti-inflammatory drug Anakinra®, Wnt inhibitor Lorecevivint®, chondroanabolic growth factor Sprifermin™, and various protease inhibitors, are discussed in detail. The limitations of commonly used OA animal models are elaborated to understand this failure better. Moreover, this review addresses the challenges of patient stratification into different endotypes and phenotypes, the consideration of subgrouping in clinical trials, and the lack of suitable clinical outcome parameters. In summary, this review highlights potential reasons for the high failure rate of DMOADs in clinical trials and outlines key points for future improvement.
Keywords: Animal models; Clinical trials; Disease-modifying osteoarthritis drugs; Drug development; Endotypes; Osteoarthritis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyaluronic acid and other conservative treatment options for osteoarthritis of the ankle.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Oct 17;2015(10):CD010643. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010643.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26475434 Free PMC article.
-
WITHDRAWN: Non-aspirin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for treating osteoarthritis of the knee.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jul 18;2006(1):CD000142. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000142.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. PMID: 17636601 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of the use of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) inhibitors, adalimumab and infliximab, for Crohn's disease.Health Technol Assess. 2011 Feb;15(6):1-244. doi: 10.3310/hta15060. Health Technol Assess. 2011. PMID: 21291629 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults and an economic evaluation of their cost-effectiveness.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Nov;10(42):iii-iv, xi-xiii, 1-229. doi: 10.3310/hta10420. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 17049139
References
-
- Alves-Simoes M (2022) Rodent models of knee osteoarthritis for pain research. Osteoarthr Cartil 30(6):802–814. 10.1016/j.joca.2022.01.010 - PubMed
-
- Anderson GP (2008) Endotyping asthma: new insights into key pathogenic mechanisms in a complex, heterogeneous disease. Lancet 372(9643):1107–1119. 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61452-X - PubMed
-
- Angelini F, Widera P, Mobasheri A, Blair J, Struglics A, Uebelhoer M, Henrotin Y, Marijnissen AC, Kloppenburg M, Blanco FJ, Haugen IK, Berenbaum F, Ladel C, Larkin J, Bay-Jensen AC, Bacardit J (2022) Osteoarthritis endotype discovery via clustering of biochemical marker data. Ann Rheum Dis 81(5):666–675. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221763 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

