Enhancing 3D dopamine transporter imaging as a biomarker for Parkinson's disease via self-supervised learning with diffusion models
- PMID: 40580955
- PMCID: PMC12281361
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102207
Enhancing 3D dopamine transporter imaging as a biomarker for Parkinson's disease via self-supervised learning with diffusion models
Abstract
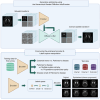
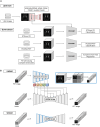
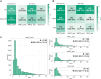
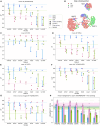
Accurate diagnosis and precise estimation of disease progression states are crucial for developing effective treatment plans for patients with parkinsonism. Although various deep learning-based computer-aided diagnostic models have demonstrated benefits, they have been relatively underexplored in parkinsonism owing to limited data and lack of external validation. We introduce the hierarchical wavelet diffusion autoencoder (HWDAE), a generative self-supervised model trained with 1,934 dopamine transporter positron emission tomography (DAT PET) images. HWDAE learns relevant disease traits during generative training, prior to supervision with human labels, as evidenced by its ability to synthesize realistic images representing different disease states of Parkinson's disease. The pretrained HWDAE is subsequently adapted for two differential diagnostic tasks and one disease progression estimation task, tested on images from two medical centers. Our training approach introduces a paradigm for deep learning research utilizing PET and expands the potential of DAT PET as a biomarker for Parkinson's disease.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; biomarker; deep learning; diffusion model; dopamine transporter; generative model; parkinsonism; positron emission tomography; self-supervised learning.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Food and Drug Administration. FDA DaT Scan Approval Letter. (2011). https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/022454Orig1s00....
-
- Summary of the European Public Assessment Report for DaTSCAN. (2011). ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/datscan#product-information-section.
-
- Hastings A., Cullinane P., Wrigley S., Revesz T., Morris H.R., Dickson J.C., Jaunmuktane Z., Warner T.T., De Pablo-Fernández E. Neuropathologic Validation and Diagnostic Accuracy of Presynaptic Dopaminergic Imaging in the Diagnosis of Parkinsonism. Neurology. 2024;102 doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000209453. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

