Co-occurrence of myositis and neuropathy after anti-CD30 therapy in a late-adolescent Hodgkin lymphoma patient
- PMID: 40581649
- PMCID: PMC12205510
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-025-02056-2
Co-occurrence of myositis and neuropathy after anti-CD30 therapy in a late-adolescent Hodgkin lymphoma patient
Abstract
Objective: Immune-related adverse events (irAEs) are recognized in oncology, particularly with immune checkpoint inhibitors and other targeted therapies. Brentuximab Vedotin (BV), is an anti-CD30 antibody-drug conjugate- its association with immune-mediated myositis remains unexplored. We report a case of an adolescent with Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) who developed neuropathy and myositis following BV therapy.
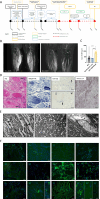
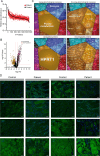
Materials & methods: The diagnostic work-up included MRI as well as microscopic analyses (histology, electron microscopy, and immunostainings including CD30 and MxA) of a gastrocnemius muscle biopsy. Proteomic analysis was also performed on the same biopsy, and paradigmatic protein dysregulations were validated through immunostaining. Serum NCAM1 levels were measured using ELISA.
Results: The patient, diagnosed with HL at 15 years, developed neuropathy after Vincristine treatment and was switched to BV. During BV therapy, she experienced progressive muscle weakness and foot drop, leading to discontinuation. MRI confirmed myositis, and biopsy revealed neurogenic and inflammatory changes with complement deposition and mitochondrial dysfunction. Proteomics showed upregulation of inflammatory relevant proteins, with HPRT1 (749.43-fold) being the most increased one. Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) therapy improved muscle strength.
Discussion: Myositis following BV therapy has not been reported. Findings suggest an immune-mediated mechanism with B-cell involvement. Given the response to IVIG, B-cell-directed therapies may be beneficial. This case identifies BV-induced myositis as a novel irAE.
Keywords: Anti-CD30; Brentuximab vedotin; Chemotherapy; Hodgkin lymphoma; Myositis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Our study was approved by the ethical committee of the University Hospital Duisburg-Essen (BO-19–9011). Consent for publication: The patient has given consent for publication of her clinical data and case description. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no compenting interests.
Figures
References
-
- Castellino SM, Pei Q, Parsons SK, Hodgson D, McCarten K, Horton T, Cho S, Wu Y, Punnett A, Dave H, Henderson TO, Hoppe BS, Charpentier A-M, Keller FG, Kelly KM (2022) Brentuximab vedotin with chemotherapy in pediatric high-risk Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med 387:1649–1660. 10.1056/NEJMOA2206660 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- PROFILNRW-2020-107-A/Ministerium für Kultur und Wissenschaft des Landes Nordrhein-Westfalen
- 01EC1901, MESINFLAME/German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF)
- B2B-RARE/European Regional Development Fund
- B2B-RARE/European Regional Development Fund
- B2B-RARE/European Regional Development Fund
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

