Insights into plastocyanin-cytochrome b6f complex formation: The role of plastocyanin phosphorylation
- PMID: 40581738
- PMCID: PMC12341890
- DOI: 10.1093/plphys/kiaf269
Insights into plastocyanin-cytochrome b6f complex formation: The role of plastocyanin phosphorylation
Abstract
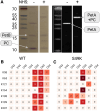
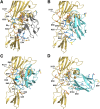
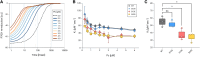
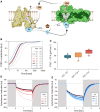
Plastocyanin (PC) is a copper-containing protein that acts as a mobile electron carrier in plants during photosynthesis. In this work, we investigated the role of PC phosphorylation in photosynthetic electron transfer, focusing on interactions with both cytochrome b6f (Cytb6f) and photosystem I (PSI) in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. While the binding and electron transfer between PC and PSI are well characterized, the interaction between PC and Cytf remains less clear. Using chemical cross-linking combined with mass-spectrometry, we identified 2 potential binding models for PC and Cytf: "side-on" and "head-on." To evaluate electron transfer, we developed an in vitro system that allowed oxidized PC, formed via light-driven electron transfer at PSI, to reoxidize Cytf. Our data show that a phosphomimetic variant of PC, where phosphorylated PC S49 residue interacts with PetA-K188, displays faster Cytf oxidation, likely optimizing binding and electron transfer between PC and Cytf. Additionally, PC phosphomimetic variants exhibited slower transfer rates than the wild type, suggesting that phosphorylation also modulates PC's interaction with PSI. This regulation likely optimizes Cytf oxidation and electron transfer under conditions of low PC availability, such as during high light stress. Overall, PC phosphorylation appears to play a role in fine-tuning electron transfer between PSI, Cytb6f, and PC, thereby ensuring efficient photosynthesis in dynamic environmental conditions.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Society of Plant Biologists.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement. None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cyanobacterial redox carriers support photosynthesis in a purple phototrophic bacterium.Biochem J. 2025 Aug 13;482(16):BCJ20253114. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20253114. Biochem J. 2025. PMID: 40663768
-
Single-molecule study of redox control involved in establishing the spinach plastocyanin-cytochrome b6f electron transfer complex.Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. 2019 Jul 1;1860(7):591-599. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2019.06.013. Epub 2019 Jun 24. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. 2019. PMID: 31247170
-
Cryo-EM structure of the spinach cytochrome b6 f complex at 3.6 Å resolution.Nature. 2019 Nov;575(7783):535-539. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1746-6. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Nature. 2019. PMID: 31723268 Free PMC article.
-
Photosynthetic Control and Its Role in Protection of Photosystem I against Photoinhibition.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2025 Jul;90(7):840-859. doi: 10.1134/S0006297925601121. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2025. PMID: 40759417 Review.
-
Comparison of self-administered survey questionnaire responses collected using mobile apps versus other methods.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jul 27;2015(7):MR000042. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000042.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26212714 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bergner SV, Scholz M, Trompelt K, Barth J, Gäbelein P, Steinbeck J, Xue H, Clowez S, Fucile G, Goldschmidt-Clermont M, et al. STATE TRANSITION7-dependent phosphorylation is modulated by changing environmental conditions, and its absence triggers remodeling of photosynthetic protein complexes. Plant Physiol. 2015:168(2):618–634. 10.1104/pp.15.00072 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

