Single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with benzimidazole resistance of the β-tubulin isotype 1 gene in Ascaris lumbricoides isolated in South Africa
- PMID: 40582181
- PMCID: PMC12266506
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjid.2025.104556
Single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with benzimidazole resistance of the β-tubulin isotype 1 gene in Ascaris lumbricoides isolated in South Africa
Abstract
Background: Ascariasis is a parasitic infection caused by Ascaris lumbricoides and infects over 1.2 billion people worldwide. Benzimidazole (BZ) drugs remain the standard treatment in large-scale deworming programs globally. The prevalence of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in the β-tubulin gene of A. lumbricoides (F200Y, E198A and F167Y) is increasing due to the widespread use of BZ drugs.
Aim: To investigate the prevalence of the above-mentioned SNPs in a South African adult population.
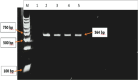
Methods: This was a sub-study of the main cross-sectional study with participants (n = 414) who had been recruited from five public health clinics in the peri‑urban areas South of Durban, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. For the current study, a purposive selection of 20 stool samples that were positive for A. lumbricoides eggs was made. A. lumbricoides worm extracts (n = 4) were used as a positive control. Sanger sequencing and RFLP-PCR were used to identify the presence of mutations.
Results: No mutations were detected, and all genotypes observed at codons F167Y, E198A and F200Y were the homozygous wild-type genotype.
Conclusion: Although no mutations were found in this small study, the potential occurrence of mutations in a larger sample subset cannot be ruled out.
Keywords: A. lumbricoides, β-tubulin isotype 1 gene; Benzimidazole drug resistance; Single nucleotide polymorphisms; Treatment efficacy.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier España, S.L.U.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Unveiling β-Tubulin Isotype-1 Polymorphisms in Haemonchus contortus from Pakistani Livestock: New Insights into Benzimidazole Resistance and Protein Structure Analysis.Acta Parasitol. 2025 Apr 29;70(3):97. doi: 10.1007/s11686-025-01037-8. Acta Parasitol. 2025. PMID: 40299249
-
Pharmacotherapies for sleep disturbances in dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Nov 16;11(11):CD009178. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009178.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 15;11:CD009178. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009178.pub4. PMID: 27851868 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions to improve water, sanitation, and hygiene for preventing soil-transmitted helminth infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jun 21;6(6):CD012199. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012199.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35726112 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid, point-of-care antigen tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 22;7(7):CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35866452 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) World Health Organization 2019. Soil-transmitted helminth infections; Geneva, Switzerland: 2020. Global Atlas of Helminth Infections: Soil-transmitted helminths.https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/soil-transmitted-helmin... [Accessed 2023 November 20]
-
- Pullan R.L., Smith J.L., Jasovsky M., Brooker S. Global, regional, and national estimates of soil-transmitted helminth soil prevalence in 2010. PLOS Neg Trop Dis. 2014;8:e2657.
-
- Centers For Disease Control. Parasites – Ascariasis. 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/ascariasis/index.html#:∼:text=An20estimate... [Accessed 2023 November 20].
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

