Impact of Obesity on Metabolic Control in Type 2 Diabetes: Five-Year Trends of Turkish Nationwide Survey of Glycemic and Other Metabolic Parameters of Patients with Diabetes (TEMD Obesity Study, 2017-2022)
- PMID: 40582352
- PMCID: PMC12503523
- DOI: 10.1159/000547136
Impact of Obesity on Metabolic Control in Type 2 Diabetes: Five-Year Trends of Turkish Nationwide Survey of Glycemic and Other Metabolic Parameters of Patients with Diabetes (TEMD Obesity Study, 2017-2022)
Abstract
Introduction: Türkiye has the highest obesity prevalence in Europe. Obesity not only causes type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) but also impairs glycemic control in patients with T2DM. There is insufficient information about the demographic and clinical differences between individuals with T2DM who are living with or without obesity. The second TEMD survey across Türkiye investigated the latest overweight and obesity prevalence in patients with T2DM. The present study evaluated the 5-year changes in the prevalence, factors associated with an obesity diagnosis, and the association between obesity and metabolic control.
Methods: Patients under follow-up in tertiary units specialized for diabetes care were consecutively enrolled. The sociodemographic, anthropometric, and clinical variables were recorded. Metabolic targets were defined as hemoglobin A1c <7%, home arterial blood pressure <135/85 mm Hg, or low-density lipoprotein cholesterol <100 mg/dL or <70 mg/dL or <55 mg/dL according to the risk factors or complications of patients. Metabolic target attainment rates were investigated across normal-weight, overweight, and obesity body mass index (BMI) classes.
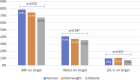
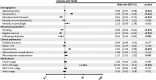
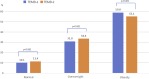
Results: The TEMD Obesity Study enrolled 4,935 patients with T2DM (age 58.9 ± 10.1 years; women 59.8%). The prevalence of overweight and obesity was 33.4% and 55.1%, respectively. Obesity was more frequent in women with T2DM than men (66.2% vs. 38.1%; p ≤ 0.001). From 2017 to 2022, the obesity rate decreased from 59.0% to 55.1%, while the overweight rate increased from 31.0% to 33.4%. As BMI class increased, the achievement of three metabolic targets decreased while the incidence of microvascular complications rose. Significant associations were found between obesity and sociodemographic characteristics (age, sex, education level) and lifestyle measures (diet, exercise, smoking) in multivariable logistic regression analysis.
Conclusion: The TEMD Obesity study showed a decrease in obesity rates among patients with T2DM between 2017 and 2022. Also, the findings suggest that obesity poses an important barrier to the achievement of metabolic goals.
Keywords: Dyslipidemia; Hemoglobin A1c; Hypertension; Obesity; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
Sinem Kiyici engaged in advisory boards and lectures with Novo Nordisk, Trispera Pharma Solutions, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Abbott, Novartis, and Sanofi and participated in clinical trial performed by Boehringer Ingelheim. Alper Sonmez participated in advisory board meetings performed by Novo Nordisk, Novartis, Eli Lilly, and Trispera. Cem Haymana participated in speakers’ bureaus performed by Sanofi, Novartis, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Serpil Salman participated in speakers’ bureaus and advisory boards conducted by AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Abdi İbrahim, and Roche Diagnostics. Meral Mert participated in speakers’ bureaus performed by Novo Nordisk, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, and Abdi İbrahim. Fahri Bayram participated in clinical studies and advisory board meetings conducted by Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, MSD, Meditronic, Trispera, Abbott, Sanovel, Sanofi, and Novartis. Volkan Demirhan Yumuk engaged in advisory boards and lectures with Novo Nordisk, Eli Lily, Rhythm, and Regeneron. Other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kopelman P. Health risks associated with overweight and obesity. Obes Rev. 2007;8(Suppl 1):13–7. - PubMed
-
- Sonmez A, Yumuk V, Haymana C, Demirci I, Barcin C, Kıyıcı S, et al. Impact of obesity on the metabolic control of type 2 diabetes: results of the Turkish nationwide survey of glycemic and other metabolic parameters of patients with diabetes mellitus (TEMD obesity study). Obes Facts. 2019;12(2):167–78. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

