Impaired Cytokine Secretion Contributes to Age-Dependent Immune Dysfunction in SARS Coronavirus Response and Is Restored by Young CD11b-Positive Cell Transfer
- PMID: 40583123
- PMCID: PMC12419839
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.70154
Impaired Cytokine Secretion Contributes to Age-Dependent Immune Dysfunction in SARS Coronavirus Response and Is Restored by Young CD11b-Positive Cell Transfer
Abstract
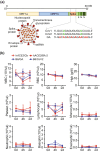
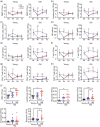
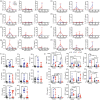
COVID-19 mortality disproportionately affects the elderly, yet the cellular and molecular factors contributing to age-related immune system remodeling remain unclear. Using SARS-CoV-derived ssRNA sequences, we modeled age-dependent immune responses in mice. Aged mice exhibited higher mortality and severe lung inflammation upon viral ssRNA challenge, mirroring clinical observations. We uncovered a pre-existing inflammatory state in aged mice, characterized by elevated baseline levels of specific immune cells and cytokines correlating with poor outcomes. Age-related immune dysfunction stemmed from impaired IRF7 signaling and defective SNARE-mediated cytokine secretion in CD11b+ cells. Notably, the adoptive transfer of young CD11b+ cells to aged mice exposed to SARS-CoV2 ssRNA reduced mortality, alleviated lung inflammation, and normalized cytokine profiles. These findings provide insights into age-related immune dysregulation during viral challenges and suggest potential therapeutic strategies for severe COVID-19 in the elderly.
Keywords: IRF7; SARS‐CoV; SNARE; aging; innate immunity.
© 2025 The Author(s). Aging Cell published by Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bonam, S. R. , Hazell N. C., Mathew M. J., et al. 2024. “Innate and Adaptive Immune Parameters Following mRNA Vaccination in Mice.” Vaccine 12, no. 5: 543. https://www.mdpi.com/2076‐393X/12/5/543. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

