Effect of Acute Administration of Caffeine on Neuropathic Pain and the Role of Nitric Oxide Pathway in an Animal Model of Chronic Constriction Injury
- PMID: 40583886
- PMCID: PMC12198742
- DOI: 10.32598/bcn.2024.5523.1
Effect of Acute Administration of Caffeine on Neuropathic Pain and the Role of Nitric Oxide Pathway in an Animal Model of Chronic Constriction Injury
Abstract
Introduction: Partial peripheral nerve injury often results in chronic pain, including hyperalgesia and allodynia. Caffeine, as a non-selective antagonist of adenosine receptors (ARs), has protective effects on neuropathic pain. Since nitric oxide (NO) is partially involved in the central effects of caffeine, we investigated the effects of acute caffeine administration on neuropathic pain, focusing on A1 and A2 receptors and the possible role of NO.
Methods: Following chronic constriction injury (CCI), male Wistar rats were administered caffeine (10, 50, and 100 mg/kg). Also, groups of animals received L-NAME (30 mg/kg) or L-arginine (100 mg/kg) either alone or before treatment with 50 mg/kg of caffeine. Rats were tested for hyperalgesia and allodynia at 4, 7, 14, 21, and 28 days following CCI.
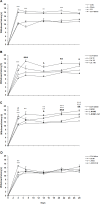
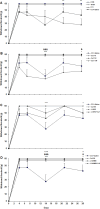
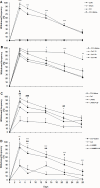
Results: Administration of 10 mg/kg of caffeine significantly increased cold allodynia, while 50 and 100 mg/kg of caffeine decreased mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia. Pre-treatment with L-NAME before caffeine administration decreased cold and mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia. Treatment with L-arginine before caffeine administration increased thermal hyperalgesia and decreased cold allodynia.
Conclusion: The present data show that caffeine dose-dependently affects the pro-analgesic or anti-analgesic states in the CCI model.
Keywords: Adenosine receptors (ARs); Caffeine; L-Arginine; L-NAME; Neuropathic pain; Nitric oxide (NO).
Copyright© 2024 Iranian Neuroscience Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rutin engages opioid/benzodiazepine receptors towards anti-neuropathic potential in a rat model of chronic constriction injury: relevance to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul;398(7):9199-9213. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03842-4. Epub 2025 Feb 6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39912904
-
Effect of Micronized Purified Flavonoid Fraction Containing Hesperidin and Diosmin on Vincristine-Induced Neuropathy in Rats; the Role of Nitric Oxide Pathway.Iran J Pharm Res. 2024 Nov 2;24(1):e154455. doi: 10.5812/ijpr-154455. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Iran J Pharm Res. 2024. PMID: 40718454 Free PMC article.
-
Corticosteroids for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 5;2016(5):CD003725. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003725.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27149418 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral and biochemical changes associated with the analgesic effects of (2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine alone and in combination with meloxicam following disk puncture in mice.Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 12;6:1574474. doi: 10.3389/fpain.2025.1574474. eCollection 2025. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40585309 Free PMC article.
-
Ketorolac for postoperative pain in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 7;7(7):CD012294. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012294.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29981164 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
