Association analysis between nutritional factors within the genome and the risk of osteoarthritis
- PMID: 40584103
- PMCID: PMC12202467
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1592974
Association analysis between nutritional factors within the genome and the risk of osteoarthritis
Abstract
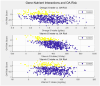
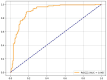
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a multifactorial disease influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. Recent studies suggest that genetic variants involved in nutrient metabolism may interact with dietary factors to modulate OA risk. Understanding these gene-nutrient interactions could inform personalized prevention strategies for OA. We conducted a cross-sectional study involving 500 participants to explore associations between specific genetic variants and OA susceptibility, considering dietary intake. Genotyping focused on polymorphisms in the FADS1 gene (rs174537) related to omega-3 fatty acid metabolism, the VDR gene (rs2228570) involved in vitamin D metabolism, and the IL-6 gene (rs1800795), a marker of inflammation. Dietary intake of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and antioxidants was assessed using validated food frequency questionnaires. Gene-nutrient interactions were evaluated using multivariable logistic regression models, adjusting for potential confounders. Individuals carrying the G allele of FADS1 who reported low omega-3 fatty acid intake exhibited a significantly increased risk of OA [Odds Ratio (OR) = 1.45; 95% Confidence Interval (CI): 1.10-1.90; = 0.01]. Similarly, participants with the TT genotype of VDR and insufficient vitamin D intake had a higher OA risk (OR = 1.55; 95% CI: 1.15-2.10; = 0.005). Furthermore, carriers of the IL-6 GG genotype with low antioxidant consumption showed elevated inflammatory markers and an increased OA risk (OR = 1.60; 95% CI: 1.20-2.15; = 0.002). Our findings indicate that specific genetic variants in FADS1, VDR, and IL-6 genes interact with dietary factors to influence OA susceptibility. These gene-nutrient interactions underscore the importance of personalized dietary interventions in mitigating OA risk. Future longitudinal studies are warranted to confirm these associations and develop tailored prevention strategies.
Keywords: FADS1 gene; gene-nutrient interactions; inflammatory markers; osteoarthritis; vitamin D receptor.
Copyright © 2025 Kang, Wu, Lin, Dai and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nutritional interventions for survivors of childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 22;2016(8):CD009678. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009678.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27545902 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and safety of vitamin D in relation to bone health.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007 Aug;(158):1-235. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007. PMID: 18088161 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidants for female subfertility.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 28;7(7):CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Aug 27;8:CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub4. PMID: 28752910 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Effects of a gluten-reduced or gluten-free diet for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 24;2(2):CD013556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35199850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen J, Meng Q. Causal role of oxidative stress-related genes in osteoarthritis. Int J Biol Life Sci. (2024) 8:28–31. doi: 10.54097/ghj4c127 - DOI
-
- Zang K, Brossard M, Wilson T, Ali SA, Espin-Garcia O. A scoping review of statistical methods to investigate colocalization between genetic associations and microRNA expression in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil Open. (2024) 6:100540–13. doi: 10.1016/j.ocarto.2024.100540, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources