Infections with Chlamydia pneumoniae and SARS-CoV-2 and Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis
- PMID: 40584180
- PMCID: PMC12202369
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1587782
Infections with Chlamydia pneumoniae and SARS-CoV-2 and Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis
Abstract
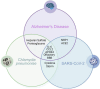
Introduction: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most prevalent neurodegenerative disease in the world, but our understanding of causation is still lacking. A current evidence-based hypothesis proposes that certain infectious agents initiate the neurodegeneration consistent with AD. Two infectious agents correlated to AD pathogenesis are Chlamydia pneumoniae (Cpn), a respiratory obligate intracellular bacterium, and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the coronavirus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. Both organisms may predispose susceptible populations to disease manifestations, such as AD.
Methods: This review focused on peer-reviewed original research and review articles evaluating the potential association of Cpn and SARS-CoV-2 with AD. Our focus included: genetic risk with expression of APOEε4 and other biomarkers common to AD including interleukin-6 (IL-6), chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2), neuropilin-1 (NRP1), and structural/functional aspects of the infectious processes and resultant neuroinflammation.
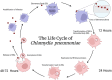
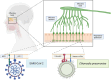
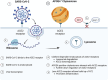
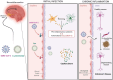
Results: Both Cpn and SARS-CoV-2 may infect the neuroepithelium of the olfactory system to enter the brain. Cpn binds to heparan sulfate proteoglycans for entry into mucosal cells. SARS-CoV-2 infects epithelia after binding to ACE2 receptors. Once inside the neuroepithelium, the pathogens may traffic to the olfactory bulbs. NRP1, an abundant receptor in AD, also potentiates SARS-CoV-2 infection. Furthermore, both pathogens may enter the systemic circulation for eventual entry through the blood brain barrier. The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, in conjunction with CCL2, co-stimulates macrophages, resulting in IL-6 cytokine release. Likewise, Cpn infection leads to an increase of CCL2 and IL-6 cytokine release. The primary infection of either organism may lead to chronically elevated levels of IL-6 and secondary infection(s). Additionally, host APOEε4 expression appears to increase susceptibility to Cpn and SARS-CoV-2 infections.
Discussion: Cpn and SARS-CoV-2 may enter the brain through olfactory neuroepithelial cells and/or through the blood brain barrier. SARS-CoV-2 utilizes specific receptors for infection, while Cpn utilizes binding of proteoglycans. Neuroinflammation may be an outcome of infection with one or both organisms as observed by increased levels of CCL2 and IL-6 leading to AD pathogenesis. Genetic risk is noted for infection with both organisms with expression of APOEε4. Ongoing and future studies will further dissect mechanisms of infection with SARS-CoV-2 and Cpn as they may inform on causation and diagnostic factors for AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Chlamydia pneumoniae; SARS-CoV-2; blood-brain barrier; neuroinflammation; olfaction.
Copyright © 2025 Romanella, McCall, Corwin, Faruq, Lingo, Bhambhani, Hammond and Balin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Measures implemented in the school setting to contain the COVID-19 pandemic.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jan 17;1(1):CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 May 2;5:CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029.pub2. PMID: 35037252 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Workplace interventions to reduce the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection outside of healthcare settings.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 6;5(5):CD015112. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015112.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Apr 10;4:CD015112. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015112.pub3. PMID: 35514111 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
SARS-CoV-2-neutralising monoclonal antibodies for treatment of COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 2;9(9):CD013825. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013825.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34473343 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody tests for identification of current and past infection with SARS-CoV-2.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 17;11(11):CD013652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013652.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36394900 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alberts B., Johnson A., Lewis J., Raff M., Roberts K., Walter P. (2002). Cell Biology of Infection: Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4th Edn. New York, NY: Garland Science.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

