The IIIVmrMLM method uncovers new genetic variants associated with resistance to Fusarium wilt in flax
- PMID: 40584242
- PMCID: PMC12202785
- DOI: 10.18699/vjgb-25-41
The IIIVmrMLM method uncovers new genetic variants associated with resistance to Fusarium wilt in flax
Abstract
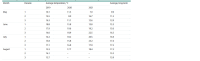
Flax (Linum usitatissimum) is an important agricultural crop grown for fiber and oil production, playing a key role in various industries such as production of paints, linoleum, food, clothes and composite materials. Fusarium wilt caused by the fungus Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lini is a reason of significant economic damage in flax cultivation. The spores of the fungus can persist in the soil for a long time, so obtaining resistant varieties is important. Here we used data on the resistance of 297 flax accessions from the collection of the Federal Center for Bast Crops in Torzhok (Russian Federation) to infection by a highly virulent isolate of the fungus MI39 in 2019-2021. Genotype resistance to infection was assessed by calculating the DSI index, a normalized proportion of genotypes with the same disease symptoms. The IIIVmrMLM program in Single_env mode was used to search for regions of the flax genome associated with resistance. The IIIVmrMLM model was designed to address methodological shortcomings in identifying all types of interactions between alleles, genes and environment, and to unbiasedly estimate their genetic effects. Being a multilocus MLM model, it estimates the effects of all genes as well as the effects of all interactions simultaneously. A total of 111 QTNs were found, of which 34 fell within the body of a known gene or were located in flanking regions within 1,000 bp. The genes into which the detected variants fell were associated with resistance to abiotic and biotic stresses, root, shoot and flower growth and development. Ten of the QTNs found mapped to regions of previously identified QTLs controlling the synthesis of palmitic, oleic, and other fatty acids. QTN Chr1_1706865/Chr1_1706872 and QTN Chr8_22542741 mark regions identified previously in an association search by the GAPIT program. The allelic effect was confirmed for all the QTNs found: a Mann-Whitney test was performed, which confirmed significant differences between the DSI index value in carriers of the reference and alternative allele. An increase in the number of alleles with negative effects in the genotype leads to a statistically significant decrease in the DSI value for all three years of testing. The groups of varieties with a large number of alleles reducing the DSI index had the best resistance. A total of 5 varieties were selected from the collection for which the number of alleles reducing the DSI index value did not exceed the number of alleles with the opposite effect for all three years. These varieties can be used further in breeding programs.
Лен (Linum usitatissimum) – важная сельскохозяйственная культура, выращиваемая для получения волокна и масла. Лен используют для производства красок, линолеума, в пищевой промышленности, для производства одежды и композитных материалов. Значительный экономический ущерб при выращивании льна наносит фузариозное увядание, вызываемое грибом Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lini. Споры гриба могут долгое время сохраняться в почве, поэтому получение устойчивых к заражению сортов имеет большое значение Здесь мы использовали данные об устойчивости 297 образцов льна из коллекции Федерального научного центра лубяных культур в Торжке (Россия) к заражению сильнo вирулентным изолятом гриба MI39 в 2019–2021 гг. Устойчивость генотипа к заражению оценивали путем вычисления индекса DSI – нормализованной пропорции генотипов с одинаковыми симптомами болезни. Для поиска районов генома льна, ассоциированных с устойчивостью, использовали программу IIIVmrMLM в режиме Single_env. Модель IIIVmrMLM была разработана для устранения методологических недостатков в выявлении всех типов взаимодействий между аллелями, генами и средой и для несмещенной оценки их генетических эффектов. Поскольку это мультилокусная MLM-модель, она оценивает эффекты всех генов, а также эффекты всех взаимодействий одновременно. Всего было найдено 111 QTN, из которых 34 были локализованы в последовательности известного гена или расположены во фланкирующих районах на расстоянии, не превышающем 1 т. п. н. Гены, в которые попадали обнаруженные варианты, были связаны с устойчивостью к абиотическим и биотическим стрессам, с ростом и развитием корня, побега и цветка. Десять из найденных QTN картировались в областях ранее идентифицированных QTL, контролирующих синтез пальмитиновой, олеиновой и других жирных кислот. QTN Chr1_1706865/ Chr1_1706872 и QTN Chr8_22542741 маркируют районы, идентифицированные нами ранее при поиске ассоциаций программой GAPIT. Для всех найденных QTN был подтвержден аллельный эффект: произведен тест Манна–Уитни, который подтвердил значимые различия между значением DSI у носителей референсного и альтернативного аллеля. Увеличение в генотипе числа аллелей с негативным эффектом приводит к статистически значимому уменьшению величины DSI для всех трех лет тестирования. Группы сортов с большим количеством аллелей, уменьшающих индекс DSI, имели наилучшую устойчивость. Всего из коллекции было выбрано пять сортов, для которых число аллелей, уменьшающих величину DSI, не превышало число аллелей с обратным эффектом по всем трем годам. Эти сорта могут быть использованы в дальнейшем в селекционных программах.
Keywords: Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lini; Fusarium wilt; GWAS; Linum usitatissimum; flax.
Copyright © AUTHORS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
