Age-related and postmenopausal breast cancer progression and treatment management: The significance of pro-inflammatory cytokines and CXC chemokines
- PMID: 40584290
- PMCID: PMC12205809
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2025.101606
Age-related and postmenopausal breast cancer progression and treatment management: The significance of pro-inflammatory cytokines and CXC chemokines
Abstract
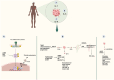
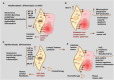
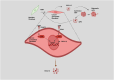
Older age is one of the leading risk indicators for advanced breast cancer. It is critical to extensively investigate how aging affects breast cancer, considering the increasing rate of population aging. Human body aging and death are caused by cellular senescence and alterations in the aging microenvironment in vivo. Breast cancer cells may invade more easily with age due to the stiff extracellular matrix of the breast. Furthermore, growing evidence suggests that the massive release of inflammatory immune mediators, such as cytokines (interleukins) or CXC chemokines (CXCs), and their receptors (CXCRs), including interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8/CXCL8, tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interferon (INF), transforming growth factor (TGF), CXCL1, CXCL9, CXCL10, CXCL11/CXCR3, and CXCL12/CXCR4, plays a critical role in the development of breast cancer in elderly patients. Researchers are particularly interested in obesity-induced inflammation because it has been shown to raise the risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women with higher body mass index. Obesity-triggered inflammation causes increased infiltration of proinflammatory cytokines, adipokines, immune cells, and tumor cells in the enlarged adipose tissue of postmenopausal women with breast cancer, thereby modulating the tumor's immune-mediated microenvironment. Therefore, in this review, we focus on the functional significance studies of proinflammatory cytokines, CXCs, and CXCRs and describe their roles in influencing breast cancer progression in older women and their factors, such as obesity in postmenopausal women. In addition, the current status and prospects of cytokine- and CXC-based theranostic interventions for breast cancer therapy in elderly and postmenopausal women are discussed.
Keywords: Age; Breast cancer; CXC chemokines; Obesity; Postmenopausal women; Pro-inflammatory cytokines; Theranostic strategies.
© 2025 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co., Ltdé.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors say they have no commercial or financial ties that could be seen as a conflict of interest in our study. Because of this, there were no conflicts of interest in the study.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Long-term hormone therapy for perimenopausal and postmenopausal women.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 17;1(1):CD004143. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004143.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28093732 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for weight reduction in obesity to improve survival in women with endometrial cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Mar 27;3(3):CD012513. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012513.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36971688 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin for women who are overweight or obese during pregnancy for improving maternal and infant outcomes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 24;7(7):CD010564. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010564.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30039871 Free PMC article.
-
Hormone replacement therapy for women previously treated for endometrial cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 May 15;5(5):CD008830. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008830.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29763969 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
References
-
- Bray F., Laversanne M., Sung H., et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(3):229–263. - PubMed
-
- Wang Q., Goldberg M.S., Labrèche F., Ho V. The association between the incidence of post-menopausal breast cancer and residential greenness. Cancer Epidemiol. 2022;76 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

