The biological roles and molecular mechanisms of m6A reader IGF2BP1 in the hallmarks of cancer
- PMID: 40584294
- PMCID: PMC12205329
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2025.101567
The biological roles and molecular mechanisms of m6A reader IGF2BP1 in the hallmarks of cancer
Abstract
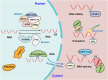
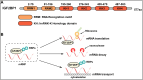
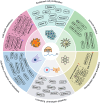
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most abundant and well-investigated internal RNA modification in eukaryotic RNAs, affecting its target gene expression by controlling RNA localization, splicing, stability, and translation. m6A modifications are regulated by m6A methyltransferase complex, demethylase, and reading proteins. Insulin-like growth factor-2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1), a member of a conserved family of single-stranded RNA-binding proteins, has recently been identified as a vital m6A reading protein. IGF2BP1 is highly expressed in various tumors and is associated with poor prognosis and treatment resistance. Furthermore, previous studies have shown that IGF2BP1 plays critical roles in regulating various cancer hallmarks, including sustained cell proliferation, cell death resistance, activation of invasion and metastasis, deregulated cellular energetics, immune evasion, and unlocking phenotypic plasticity. IGF2BP1 could promote the expression of cancer-related genes by recognizing their m6A sites, thereby altering cell characteristics, and eventually, malignancy. Therefore, IGF2BP1 might be a potential target for tumor diagnosis and anti-tumor therapeutic strategies. This review summarizes the current knowledge on the functional roles and underlying molecular mechanisms of IGF2BP1 in regulating cancer hallmarks. Moreover, we discuss the prospects of IGF2BP1 as a potential tumor diagnosis marker, as well as a potential target for an anti-tumor therapeutic strategy.
Keywords: Cancer hallmarks; IGF2BP1; Molecular therapy; m6A modification reader.
© 2025 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co., Ltdé.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel landscapes of N6-methyladenosine modification of mitochondrial oxidative stress in organ fibrosis.Eur J Pharmacol. 2025 Sep 15;1003:177888. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177888. Epub 2025 Jul 1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40609613 Review.
-
KIAA1429 facilitates metastasis via m6A-YTHDC1-dependent RND3 down-regulation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Cancer Lett. 2024 Mar 1;584:216598. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216598. Epub 2024 Jan 14. Cancer Lett. 2024. PMID: 38224863
-
RNA modifications in female reproductive physiology and disease: emerging roles and clinical implications.Hum Reprod Update. 2025 Jul 1;31(4):333-360. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmaf005. Hum Reprod Update. 2025. PMID: 40152541 Review.
-
Cuproptosis: a novel therapeutic mechanism in lung cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2025 Jun 24;25(1):231. doi: 10.1186/s12935-025-03864-1. Cancer Cell Int. 2025. PMID: 40555995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martinez C.A., Marteinsdottir I., Josefsson A., Sydsjö G., Theodorsson E., Rodriguez-Martinez H. Epigenetic modifications appear in the human placenta following anxiety and depression during pregnancy. Placenta. 2023;140:72–79. - PubMed
-
- Wu Z., Zhang W., Qu J., Liu G.H. Emerging epigenetic insights into aging mechanisms and interventions. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2024;45(2):157–172. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

