Down-regulation of neuregulin2 (NRG2) following spinal cord injury in C57BL/6 mice: Its implications in therapeutic potential
- PMID: 40584443
- PMCID: PMC12203818
- DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2025.83787.18131
Down-regulation of neuregulin2 (NRG2) following spinal cord injury in C57BL/6 mice: Its implications in therapeutic potential
Abstract
Objectives: This study aims to elucidate the alterations in neuregulin 2 (NRG2) and its receptor ErbB4 following spinal cord injury (SCI), as well as to investigate the neuroprotective mechanisms of NRG2 in neurons.
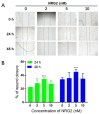
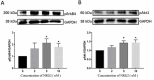
Materials and methods: Dataset GSE93561 was analyzed to verify the changes of NRG2-ErbB4 signaling pathway in mice following SCI. The levels of Iba-1 and NRG2 were analyzed by immunohistochemistry, and NRG2 and pErbB4 protein levels were detected by western blot. HT22 cells were scratched and treated with NRG2 dosed from 0-5 nM. Cell mobility was measured at the time point of 0, 24, and 48 hr after scratch. Additionally, western blot was used to detect the protein levels of pErbB4 and pAkt1 at 48 hr.
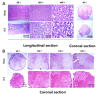
Results: By analyzing dataset GSE93561, NRG1, NRG2, and NRG3 were found to be decreased to different degrees post-SCI in mice. The results of immunohistochemistry showed that the level of Iba-1 in the injured core area was significantly increased 8 weeks post-SCI. Western blot analysis showed that the protein levels of NRG2 and pErbB4 were decreased significantly post-SCI. NRG2 promoted HT22 cell migration and dose-dependently increased pErbB4 and pAkt1 protein levels at doses ranging from 0-5 nM.
Conclusion: The NRG2-ErbB4 signaling pathway was inhibited after SCI in mice. NRG2 promotes the healing of HT22 cells after scratch injury, and the mechanism of NRG2 in the treatment of SCI may be ascribed to the activation of PI3K-Akt signaling pathways downstream to NRG2.
Keywords: C57BL/6 mouse; Migration; NRG2; Nerve regeneration; PI3K-Akt; Spinal cord injury (SCI).
© 2025. This work is openly licensed via CC BY 4.0.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Effect of removing microglia from spinal cord on nerve repair after spinal cord injury in mice].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025 Jun 15;39(6):754-761. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202503099. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40545466 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Neuroprotective Role of THBS2 in Experimental Spinal Cord Injury Via its Anti-neuroinflammatory and Anti-apoptotic Properties.Biochem Genet. 2025 Jun 26. doi: 10.1007/s10528-025-11160-w. Online ahead of print. Biochem Genet. 2025. PMID: 40571842
-
miR-210 Regulates Autophagy Through the AMPK/mTOR Signaling Pathway, Reduces Neuronal Cell Death and Inflammatory Responses, and Enhances Functional Recovery Following Cerebral Hemorrhage in Mice.Neurochem Res. 2025 Jun 5;50(3):180. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04434-7. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40471451 Free PMC article.
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Levetiracetam add-on for drug-resistant focal epilepsy: an updated Cochrane Review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Sep 12;2012(9):CD001901. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001901.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22972056 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Silva NA, Sousa N, Reis RL, Salgado AJ. From basics to clinical: A comprehensive review on spinal cord injury. Prog Neurobiol. 2014;114:25–57. - PubMed
-
- Ackery A, Tator C, Krassioukov A. A global perspective on spinal cord injury epidemiology. J Neurotrauma. 2004;21:1355–1370. - PubMed
-
- Krityakiarana W, Zhao PM, Nguyen K, Gomez-Pinilla F, Kotchabhakdi N, de Vellis J, et al. Erratum to: Proof-of concept that an acute trophic factors intervention after spinal cord injury provides an adequate niche for neuroprotection, recruitment of nestin-expressing progenitors and regeneration. Neurochem Res. 2016;41:1844. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Thuret S, Moon LD, Gage FH. Therapeutic interventions after spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:628–643. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
