Development of reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification-based assay for rapid and specific detection of human fungal pathogen, Candida auris
- PMID: 40584605
- PMCID: PMC12205917
- DOI: 10.22034/cmm.2024.345284.1572
Development of reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification-based assay for rapid and specific detection of human fungal pathogen, Candida auris
Abstract
Background and purpose: Due to the ability of Candida auris, a multidrug-resistant human fungal pathogen, to colonize the skin and hospital surfaces, it is pertinent to control its nosocomial outbreaks through rapid diagnosis. Delayed and improper diagnosis of C. auris due to misidentification becomes a major hurdle in the prevention of employment of efficient therapeutics leading to the development of drug resistance. The culture-based methods are slow and less sensitive while PCR-based methods are costly. Loop-mediated amplification (LAMP) is a feasible alternative, but it fails to differentiate between live and dead cells. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic efficiency of the reverse transcription (RT) LAMP approach and compare it with that of the LAMP assay for the detection of C. auris.
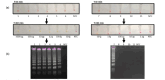
Materials and methods: RT-LAMP method was developed for the detection of C. auris and its clinical isolates. The limit of detection (LOD), sensitivity, and specificity were evaluated for the developed method using culture RNA. The RT-LAMP reaction for C. auris detection was standardized using the primers of a specific 869-bp DNA segment (accession no. XM_018317007), encoding a pyruvate: ferredoxin oxidoreductase domain, from the genome of C. auris.
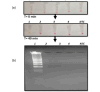
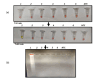
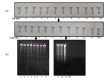
Results: The LOD for the RT-LAMP method was 1ag contrary to 10fg for LAMP method using DNA. Specificity was 100% as determined using a gram-negative bacteria and several other Candida species. The RT-LAMP method was intraspecific and displayed no cross reaction even with closely related Candida species. The RT-LAMP method was validated on 10 clinical isolates of C. auris and showed 100% concordance with a culture-based method.
Conclusion: The RT-LAMP-based method in the present study offered a proof of concept that warrants clinical validation on a large number of samples. Therefore, its diagnostic potential for the rapid, sensitive, and specific detection of C. auris could be further exploited in resource-limited regions.
Keywords: Loop-mediated isothermal amplification; RT-LAMP; Sensitivity; Specificity; Candida auris.
Copyright: © 2021, Published by Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences on behalf of Iranian Society of Medical Mycology and Invasive Fungi Research Center.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest is declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Colorimetric RT-LAMP for SARS-CoV-2 detection from nasopharyngeal swabs or crude saliva: a multicountry diagnostic accuracy study in Africa.Lancet Glob Health. 2025 Jul;13(7):e1258-e1267. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(25)00150-0. Lancet Glob Health. 2025. PMID: 40580991 Free PMC article.
-
PD-LAMP smartphone detection of SARS-CoV-2 on chip.Anal Chim Acta. 2022 Apr 22;1203:339702. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2022.339702. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Anal Chim Acta. 2022. PMID: 35361434 Free PMC article.
-
Development of rapid and simple detection of bean common mosaic virus (BCMV) in mung beans (Vigna radiata) using reverse transcription-loop mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP).Virusdisease. 2025 Mar;36(1):60-67. doi: 10.1007/s13337-025-00916-y. Epub 2025 Mar 28. Virusdisease. 2025. PMID: 40290764
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic test accuracy and cost-effectiveness of tests for codeletion of chromosomal arms 1p and 19q in people with glioma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Mar 2;3(3):CD013387. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013387.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35233774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO fungal priority pathogens list to guide research, development and public health action. World Health Organization. 2022
-
- Satoh K, Makimura K, Hasumi Y, Nishiyama Y, Uchida K, Yamaguchi H. Candida auris sp. nov., a novel ascomycetous yeast isolated from the external ear canal of an inpatient in a Japanese hospital. Microbiol Immunol. 2009;53(1):41–4. - PubMed
-
- Iguchi S, Itakura Y, Yoshida A, Kamada K, Mizushima R, Arai Y, et al. Candida auris: A pathogen difficult to identify, treat, and eradicate and its characteristics in Japanese strains. J Infect Chemother. 2019;25(10):743–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
