Hypoxia alters the response of ovarian cancer cells to the mitomycin C drug
- PMID: 40584967
- PMCID: PMC12202450
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1575134
Hypoxia alters the response of ovarian cancer cells to the mitomycin C drug
Abstract
Introduction: Discrepancies between preclinical tests and clinical results raise serious concerns about the appropriateness of the current methodologies. In particular, cell biology approaches neglect fundamental physical parameters despite their relevance to in vivo conditions. Oxygen availability is critical for cell reactions; thus, the lack of consideration of hypoxia as the main regulator of the tumor microenvironment (TME) leads to misinterpreted data with consequences for translational applications. In this study, we show that mitomycin C (MMC), an antineoplastic antibiotic, is rarely used in ovarian cancer (OC) treatment despite its potential efficacy; we use MMC as an example of a treatment that warrants reevaluation under microenvironmental conditions, particularly during in vitro testing.
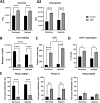
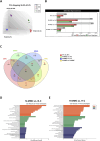
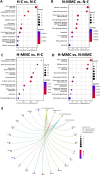
Methods: To evaluate the effects of MMC and oxygen tension (pO2) on OC cells (SKOV3), HTA 2.0 microarrays were used, which demonstrated that hypoxia and MMC induced transcriptomic changes in OC cells. Their combination particularly emphasized the effect of pO2 modification on MMC activity. The most significant findings were verified in three other OC cell lines, namely, TOV112D, ES-2, and A2780.
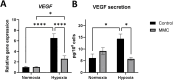
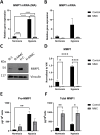
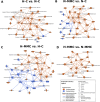
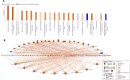
Results: Under normoxic conditions, MMC mostly affected several pathways associated with ribosome-related processes, whereas under hypoxic conditions, it induced modifications in the extracellular matrix (ECM). The most significantly upregulated gene in response to hypoxia-MMC treatment was MMP1, regulated by both MMC and hypoxia. Low pO2 levels during MMC treatment allowed the identification of important regulators, such as SPP1, and the corresponding processes, including cholesterol biosynthesis.
Conclusion: Hypoxia modulated the effects of MMC on OC cells and identified genes that may serve as promising targets to enhance the effectiveness of MMC treatment.
Keywords: differential gene expression; hypoxia; mitomycin c; ovarian cancer; pathway analysis; transcriptome.
Copyright © 2025 Gawrylak, Brodaczewska, Iwanicka-Nowicka, Koblowska, Synowiec, Bodnar, Szczylik, Lesyng, Stec and Kieda.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intravesical electromotive drug administration for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 12;9(9):CD011864. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011864.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28898400 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
References
-
- Bogani G., Matteucci L., Tamberi S., Arcangeli V., Ditto A., Maltese G., et al. (2017). The impact of number of cycles of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on survival of patients undergoing interval debulking surgery for stage IIIC-IV unresectable ovarian cancer: results from a multi-institutional study. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 27 (9), 1856–1862. 10.1097/IGC.0000000000001108 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

