KD_MultiSucc: incorporating multi-teacher knowledge distillation and word embeddings for cross-species prediction of protein succinylation sites
- PMID: 40585181
- PMCID: PMC12202750
- DOI: 10.1093/biomethods/bpaf041
KD_MultiSucc: incorporating multi-teacher knowledge distillation and word embeddings for cross-species prediction of protein succinylation sites
Abstract
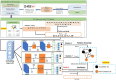
Protein succinylation is a vital post-translational modification (PTM) that involves the covalent attachment of a succinyl group (-CO-CH2-CH2-CO-) to the lysine residue of a protein molecule. The mechanism underlying the succinylation process plays a critical role in regulating protein structure, stability, and function, contributing to various biological processes, including metabolism, gene expression, and signal transduction. Succinylation has also been associated with numerous diseases, such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic syndromes. Due to its important roles, the accurate prediction of succinylation sites is essential for a comprehensive understanding of the mechanisms underlying succinylation. Although research on the identification of protein succinylation sites has been increasing, experimental methods remain time-consuming and costly, underscoring the need for efficient computational approaches. In this study, we present KD_MultiSucc, a model for cross-species prediction of succinylation sites using Multi-Teacher Knowledge Distillation and Word Embedding. The proposed method leverages the strengths of both Knowledge Distillation and Word Embedding techniques to reduce computational complexity while maintaining high accuracy in predicting protein succinylation sites across species. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed predictor outperforms existing predictors, providing a valuable contribution to PTM research and biomedical applications. To assist readers and researchers, the codes and resources related to this work have been made freely accessible on GitHub at https://github.com/nuinvtnu/KD_MultiSucc/.
Keywords: bi-direction long short-term memory (Bi-LSTM); convolutional neural network (CNN); knowledge distillation; natural language processing (NLP); succinylation; word embedding.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Active body surface warming systems for preventing complications caused by inadvertent perioperative hypothermia in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 21;4(4):CD009016. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009016.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27098439 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
