This is a preprint.
An Integrated Framework for Automated Image Segmentation and Personalized Wall Stress Estimation of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
- PMID: 40585219
- PMCID: PMC12204491
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-6630234/v1
An Integrated Framework for Automated Image Segmentation and Personalized Wall Stress Estimation of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
Abstract
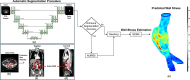
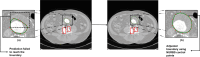
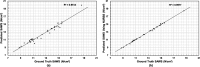
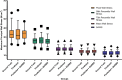
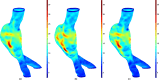
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) remains a significant public health challenge, with an 82.1% increase in related fatalities from 1990 to 2019. In the United States alone, AAA complications resulted in an estimated 13,640 deaths between 2018 and 2021. In clinical practice, computed tomography angiography (CTA) is the primary imaging modality for monitoring and pre-surgical planning of AAA patients. CTA provides high-resolution vascular imaging, enabling detailed assessments of aneurysm morphology and informing critical clinical decisions. However, manual segmentation of CTA images is labor intensive and time consuming, underscoring the need for automated segmentation algorithms, particularly when feature extraction from clinical images can inform treatment decisions. We propose a framework to automatically segment the outer wall of the abdominal aorta from CTA images and estimate AAA wall stress. Our approach employs a patch-based dilated modified U-Net model to accurately delineate the outer wall boundary of AAAs and and Nonlinear Elastic Membrane Analysis (NEMA) to estimate their wall stress. We further integrate Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines (NURBS) to refine the segmentation. During prediction, our deep learning architecture requires 17 ° 0.02 milliseconds per frame to generate the final segmented output. The latter is used to provide critical insight into the biomechanical state of stress of an AAA. This modeling strategy merges advanced deep learning architecture, the precision of NURBS, and the advantages of NEMA to deliver a robust, accurate, and efficient method for computational analysis of AAAs.
Conflict of interest statement
Additional Declarations: Competing interest reported. M.R. and the other authors declare that they have no competing interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to in uence the work reported in this manuscript. M.K.E. declares that he has a paid consultancy with W.L. Gore and Boston Scienti c. Competing interest: M.R. and the other authors declare that they have no competing interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this manuscript. M.K.E. declares that he has a paid consultancy with W.L. Gore and Boston Scientific.
Figures



References
-
- Kurugol S., San Jose Estepar R., Ross J. & Washko G. R. Aorta segmentation with a 3d level set approach and quantification of aortic calcifications in non-contrast chest ct. In 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2343–2346, DOI: 10.1109/EMBC.2012.6346433 (2012). - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

