Effect of surfactants and polymer composition on the characteristics of polyhydroxyalkanoate nanoparticles
- PMID: 40585414
- PMCID: PMC12205925
- DOI: 10.5599/admet.2723
Effect of surfactants and polymer composition on the characteristics of polyhydroxyalkanoate nanoparticles
Abstract
Background and purpose: Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) are biodegradable polyesters of bacterial origin that are actively studied as matrices for the preparation of nanoparticulate drug delivery systems. The most significant parameters affecting PHAs nanoparticles (NPs) characteristics are polymer composition and the type of surfactant used to stabilize the emulsion during NPs preparation. However, there are only a few studies in the literature investigating the effect of these factors on the characteristics of PHA NPs.
Experimental approach: Blank poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (P3HB) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (P3HBV) NPs were produced and characterized in terms of their size, morphology and zeta potential. Poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) with various molecular weights (31-50 and 85-124 kDa), as well as Tween 20 (TW20), Tween 80 (TW80), sodium deoxycholate (SDC) and sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS) were used as surfactants. For NPs that formed stable aqueous suspensions and had the most desirable characteristics (P3HB/PVA31-50 and P3HBV/PVA31-50), hemolytic activity and cytotoxicity to HeLa and C2C12 cells in vitro were determined.
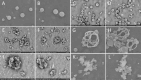
Key results: NPs of both P3HB and P3HBV obtained using PVA with the M w of 31-50 kDa as a surfactant had regular spherical shape, uniform size distribution, average diameter of about 900 nm and zeta potential of -28.5 and -28.7 mV, respectively. PVA85-124, TW20 and TW80, as well as SDC and SDS as surfactants, did not show satisfactory results due to suspension gelation, formation of hollow NPs with irregular shape and poor resuspension after washing and freeze-drying, respectively. P3HB/PVA31-50 and P3HBV/PVA31-50 NPs did not have hemolytic activity and did not show pronounced cytotoxicity to HeLa and C2C12 cells in the concentration range from 10 to 500 μg mL-1, so these samples were regarded as safe and biocompatible.
Conclusion: In this study, the effect of various non-ionic and anionic surfactants on the characteristics of P3HB and P3HBV NPs was investigated. PVA31-50 was found to be effective in producing NPs of both studied polymers with good biocompatibility and favorable characteristics, making them suitable for drug delivery applications. In contrast, other studied surfactants, i.e., PVA85-124, TW20, TW80, SDC and SDS, require further investigation. The obtained findings may promote the development of novel PHA-based nanomedicines.
Keywords: P3HB; P3HBV; Tween 80; polyvinyl alcohol; sodium deoxycholate; sodium dodecyl sulphate.
Copyright © 2025 by the authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chauhan M., Sonali, Shekhar S., Yadav B., Garg V., Dutt R., Mehata A.K., Goswami P., Koch B., Muthu M.S., Singh R.P.. AS1411 aptamer/RGD dual functionalized theranostic chitosan-PLGA nanoparticles for brain cancer treatment and imaging. Biomaterials Advances 160 (2024) 213833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioadv.2024.213833 10.1016/j.bioadv.2024.213833 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ganguly S., Dewanjee S., Sen R., Chattopadhyay D., Ganguly S., Gaonkar R., Debnath M.C.. Apigenin-loaded galactose tailored PLGA nanoparticles: A possible strategy for liver targeting to treat hepatocellular carcinoma. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 204 (2021) 111778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2021.111778 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2021.111778 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rouhi A.A., Valizadeh A., Sedghizadeh N., Beba L., Dadashi H., Kazempour M., Adibkia K., Vandghanooni S., Eskandani M.. Targeted therapy of gastric cancer with gingerol-loaded hyaluronic acid/PEG-coated PLGA nanoparticles: Development and physicochemical evaluation. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 97 (2024) 105734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2024.105734 10.1016/j.jddst.2024.105734 - DOI
-
- Mekseriwattana W., Phungsom A., Sawasdee K., Wongwienkham P., Kuhakarn C., Chaiyen P., Katewongsa K.P.. Dual Functions of Riboflavin-functionalized Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles for Enhanced Drug Delivery Efficiency and Photodynamic Therapy in Triple-negative Breast Cancer Cells. Photochemistry and Photobiology 97 (2021) 1548-1557. https://doi.org/10.1111/php.13464 10.1111/php.13464 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Du Z., Mao Y., Zhang P., Hu J., Fu J., You Q., Yin J.. TPGS-Galactose-Modified Polydopamine Co-delivery Nanoparticles of Nitric Oxide Donor and Doxorubicin for Targeted Chemo-Photothermal Therapy against Drug-Resistant Hepatocellular Carcinoma. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 13 (2021) 35518-35532. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c09610 10.1021/acsami.1c09610 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
