Molecular Mechanisms, Endurance Athlete, and Synergistic Therapeutic Effects of Marine-Derived Antioxidant Astaxanthin Supplementation and Exercise in Cancer, Metabolic Diseases, and Healthy Individuals
- PMID: 40585493
- PMCID: PMC12204856
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.70470
Molecular Mechanisms, Endurance Athlete, and Synergistic Therapeutic Effects of Marine-Derived Antioxidant Astaxanthin Supplementation and Exercise in Cancer, Metabolic Diseases, and Healthy Individuals
Abstract
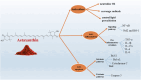
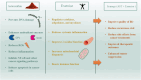
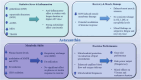
Marine-derived antioxidant astaxanthin (AST), a potent antioxidant carotenoid, has gained significant attention for its potential therapeutic effects in various diseases, including cancer and metabolic disorders. When combined with exercise, which is a well-established intervention for improving health, these two modalities may offer synergistic benefits that extend beyond their individual effects. This review explores the molecular mechanisms underlying the synergistic therapeutic effects of AST and exercise in cancer, metabolic diseases, and healthy individuals. AST exerts its beneficial effects primarily through its ability to reduce oxidative stress, modulate inflammation, and enhance cellular signaling pathways, including those involved in apoptosis, autophagy, and mitochondrial function. It has been shown to suppress tumor growth, improve insulin sensitivity, and protect against the adverse effects of chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular complications and neurodegenerative conditions. Similarly, exercise induces a wide array of molecular adaptations, including the activation of key metabolic pathways, enhancement of mitochondrial biogenesis, and modulation of inflammatory responses. These effects improve metabolic health, reduce cancer risk, and promote overall well-being. The combination of AST supplementation and exercise may provide a more potent therapeutic strategy, targeting multiple molecular pathways simultaneously. This synergy may not only enhance the effectiveness of each intervention but also reduce the side effects commonly associated with pharmacological treatments. This review discussed the current evidence for the synergistic effects of AST and exercise, highlighted the molecular mechanisms involved, and suggested potential clinical applications for these interventions in cancer, metabolic diseases, and healthy populations.
Keywords: astaxanthin; cancer; cognitive function; exercercise; molecular signaling.
© 2025 The Author(s). Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Survivor, family and professional experiences of psychosocial interventions for sexual abuse and violence: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Oct 4;10(10):CD013648. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013648.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36194890 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Selenium for preventing cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 29;1(1):CD005195. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005195.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29376219 Free PMC article.
-
Physical activity and exercise for chronic pain in adults: an overview of Cochrane Reviews.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 24;4(4):CD011279. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011279.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28436583 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

