A Rare Complication of Dental Care: A Case of Subcutaneous Emphysema, Pneumomediastinum, and Pneumopericardium
- PMID: 40585703
- PMCID: PMC12206070
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.85035
A Rare Complication of Dental Care: A Case of Subcutaneous Emphysema, Pneumomediastinum, and Pneumopericardium
Abstract
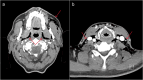
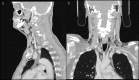
This article reports the rare case of a 64-year-old man who presented at the emergency department with interscapular pain following a dental procedure. Imaging revealed subcutaneous emphysema, pneumomediastinum, and pneumopericardium, resulting from the use of an air-driven tool during the treatment of a molar implant. Although uncommon, such iatrogenic complications can lead to serious consequences and should be promptly recognized and managed in emergency settings to prevent further deterioration.
Keywords: air-driven dental tools; dental procedure complications; pneumomediastinum; pneumopericardium; subcutaneous emphysema.
Copyright © 2025, Henin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pneumomediastinum With Mediastinitis Following Third Molar Extraction With a High-Speed Air Handpiece: A Case Report and Literature Review.Cureus. 2025 May 23;17(5):e84695. doi: 10.7759/cureus.84695. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40546478 Free PMC article.
-
A Rare Complication during Vaginal Delivery, Hamman's Syndrome: A Case Report and Systematic Review of Case Reports.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Apr 12;19(8):4618. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19084618. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35457486 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous pneumomediastinum and subcutaneous emphysema as a complication of asthma in children: case report and literature review.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2016 Oct;10(5):402-9. doi: 10.1177/1753465816657478. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2016. PMID: 27585598 Free PMC article.
-
Radiographic Convergence: A Case of Pneumomediastinum, Pneumothorax, Pneumopericardium, and Subcutaneous Emphysema.J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2025 Jan-Dec;13:23247096251367550. doi: 10.1177/23247096251367550. Epub 2025 Aug 27. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40866007 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic prophylaxis for preventing bacterial endocarditis following dental procedures.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 10;5(5):CD003813. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003813.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35536541 Free PMC article.
References
-
- John Safar, DDS DDS, MAGD MAGD. Complications after dental treatment. Reviewed/Revised Nov. [ Feb; 2025 ]. 2024. https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/mouth-and-dental-disorders/urgent-dental... https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/mouth-and-dental-disorders/urgent-dental...
-
- Subcutaneous emphysema after dental or stomatological treatment, rare complications or consequences of malpractice? [Article in French] Bodet C, Jaumotte M, Le Clercq M, Pepinster F, Gilon Y. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36354223/ Rev Med Liege. 2022;77:635–636. - PubMed
-
- Subcutaneous emphysema: dental causes and management. [ Mar; 2025 ]. 2022. https://www.oralhealthgroup.com/features/subcutaneous-emphysema-dental-c... https://www.oralhealthgroup.com/features/subcutaneous-emphysema-dental-c...
-
- Iatrogenic subcutaneous emphysema of dental and surgical origin: a literature review. McKenzie WS, Rosenberg M. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;67:1265–1268. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
