A Comparison of SGLT2 or DPP-4 Inhibitor Monotherapy vs Placebo for Type 2 Diabetes in Adolescents vs Young Adults
- PMID: 40585887
- PMCID: PMC12206083
- DOI: 10.1210/jendso/bvaf085
A Comparison of SGLT2 or DPP-4 Inhibitor Monotherapy vs Placebo for Type 2 Diabetes in Adolescents vs Young Adults
Abstract
Context: There is an unmet need for type 2 diabetes (T2D) treatments in addition to metformin and insulin for adolescents. This is due to the challenges of monotherapy in youth with T2D and need for treatment escalation to maintain glycemic control in youth generally more so than in young adults.
Objective: We assessed the efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) or dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor monotherapies in adolescents and young adults with T2D not on active therapy.
Methods: Drug-naïve adolescents and those not on active therapy received the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin, the DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin, or placebo for 26 weeks; young adults with no antidiabetic background therapy received empagliflozin, the DPP-4 inhibitor sitagliptin, or placebo for 24 weeks. The primary endpoint was treatment failure occurrence. Secondary outcomes assessed glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), fasting plasma glucose, and weight.
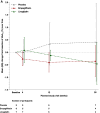
Results: Treatment failure rates were similar for empagliflozin and linagliptin vs placebo in adolescents, but significantly reduced with empagliflozin in young adults (P = .017). Empagliflozin modestly reduced mean HbA1c vs placebo in adolescents (-0.35% vs 0.41%) compared with greater reductions in young adults (-1.01% vs -0.30%). No new safety signals were identified.
Conclusion: Empagliflozin reduced HbA1c in adolescents and young adults; however, these results highlight the challenges of monotherapy for youth with T2D and need for further studies.
Keywords: DPP inhibitor; SGLT2 inhibitor; adolescents/children; empagliflozin; monotherapy; type 2 diabetes.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
