Delivery of a Muscle-Targeted Adeno-Associated Vector Via Ex Vivo Normothermic Perfusion Is Efficient, Durable, and Safe in a Preclinical Porcine Heart Transplant Model
- PMID: 40585889
- PMCID: PMC12203020
- DOI: 10.3389/ti.2025.13971
Delivery of a Muscle-Targeted Adeno-Associated Vector Via Ex Vivo Normothermic Perfusion Is Efficient, Durable, and Safe in a Preclinical Porcine Heart Transplant Model
Abstract
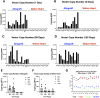
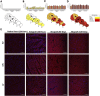
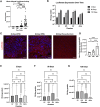
Normothermic ex-vivo organ perfusion (EVP) systems not only provide a physiological environment that preserves donor organ function outside the body but may also serve as platforms for ex-vivo organ modification via gene therapy. In this study, we demonstrated that a rationally designed muscle-tropic recombinant AAV, AAV-SLB101, delivered to the donor heart during brief normothermic EVP achieves durable cardiac transgene expression out to 90 and 120 days post-transplant in a porcine preclinical model. Moreover, transgene expression was detectable as early as 48 h post-transplant. Histological and MRI analyses of the donor myocardium showed no functional or structural impact on the allograft and no off-target gene expression in the recipient. This work will serve as a critical foundation to inform translational studies with therapeutic transgenes to improve allo-, xeno-, and auto-heart transplant outcomes.
Keywords: adeno-associated virus vector; ex vivo heart preservation; gene therapy; heart transplantation; transgene durability.
Copyright © 2025 Dewan, Chen, Lobo, Gross, Wang, Rivera, Tran, Ngeve, Johnston, Wendell, Glass, Evans, Ho, Lezberg, Casy, Bazile, Patel, Cockrell, Milano and Bowles.
Conflict of interest statement
CM has received stock compensation for serving as a consult for TransMedics Inc. WC, MB, KP, and AC are employees and shareholders of Solid Biosciences Inc. PL is an employee of TransMedics, Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Khush KK, Cherikh WS, Chambers DC, Harhay MO, Hayes D, Jr, Hsich E, et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-Sixth Adult Heart Transplantation Report - 2019; Focus Theme: Donor and Recipient Size Match. J Heart Lung Transpl (2019) 38(10):1056–66. 10.1016/j.healun.2019.08.004 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mendiola Pla M, Chiang Y, Roan J-N, Bowles DE. Gene Therapy for Cardiac Transplantation. London, United Kingdom: IntechOpen; (2022).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

