Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviate radiation induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the protein kinase B/nuclear factor kappa B pathway
- PMID: 40585959
- PMCID: PMC12203132
- DOI: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i6.106488
Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviate radiation induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the protein kinase B/nuclear factor kappa B pathway
Abstract
Background: Radiation induced pulmonary fibrosis (RIPF) is a long-term lung condition with a bleak outlook and few treatment possibilities. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)-derived exosomes (MSCs-exosomes) possess tissue repair and regenerative properties, but their exact mechanisms in RIPF remain unclear. This study explores whether MSCs-exosomes can alleviate RIPF by modulating inflammation, extracellular matrix (ECM) accumulation, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) via the protein kinase B (Akt)/nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway.
Aim: To assess the therapeutic potential and mechanisms of MSCs-exosomes in RIPF.
Methods: Sprague-Dawley rats were received 30 Gy X-ray radiation on the right chest to induce RIPF, while RLE-6TN and BEAS-2B cell lines were exposed to 10 Gy X-rays. Using differential centrifugation, MSCs-exosomes were isolated, and their protective effects were examined both in vivo and in vitro. Inflammatory cytokine concentrations were measured using Luminex liquid chip detection and enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. ECM and EMT-related proteins were analyzed using immunohistochemistry, western blotting, and real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Western blotting and immunohistochemistry were also used to investigate the mechanisms underlying MSCs-exosomes' effects in RIPF.
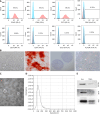
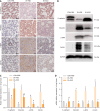
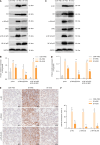
Results: Administration of MSCs-exosomes significantly mitigated RIPF, reduced collagen deposition, and decreased levels of various inflammatory cytokines. Additionally, MSCs-exosomes prevented radiation-induced ECM accumulation and EMT. Treatment with MSCs-exosomes notably promoted cell proliferation, suppressed inflammation, and reversed ECM deposition and EMT in radiation-exposed alveolar epithelial cells. Mechanistic analysis further revealed that MSCs-exosomes exerted their anti-RIPF effects by inhibiting the Akt/NF-κB pathway, as shown in both in vivo and in vitro models.
Conclusion: MSCs-exosomes mitigate RIPF by suppressing inflammation, ECM deposition, and EMT through Akt/NF-κB inhibition, highlighting their potential as a therapeutic strategy.
Keywords: Exosomes; Mesenchymal stem cells; Nuclear factor kappa B; Protein kinase B; Radiation induced pulmonary fibrosis.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-secreted KGF ameliorates acute lung injury via the Gab1/ERK/NF-κB signaling axis.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Jul 10;30(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00757-z. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40640718 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal CBLB ameliorates infantile pneumonia progression probably by ubiquitinating MAPK14.J Inflamm (Lond). 2025 Jun 19;22(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12950-025-00450-0. J Inflamm (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40537786 Free PMC article.
-
Captopril alleviates radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis by suppressing PAI-1 expression and cytoskeleton-dependent epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.Eur J Pharmacol. 2025 Aug 6;1005:178045. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.178045. Online ahead of print. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40780595
-
Association between Mesenchymal Stem Cells and COVID-19 Therapy: Systematic Review and Current Trends.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jun 22;2022:9346939. doi: 10.1155/2022/9346939. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35782071 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li J, Wang R, Shi W, Chen X, Yi J, Yang X, Jin S. Epigenetic regulation in radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Radiat Biol. 2023;99:384–395. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

