Treatment and Survival Outcomes in Rhino-Orbital Mucormycosis with and without Orbital Exenteration: A Retrospective Case Series and Literature Review
- PMID: 40585964
- PMCID: PMC12205758
- DOI: 10.2147/IMCRJ.S530233
Treatment and Survival Outcomes in Rhino-Orbital Mucormycosis with and without Orbital Exenteration: A Retrospective Case Series and Literature Review
Abstract
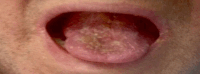
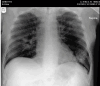
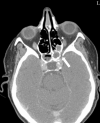
Rhino-orbital mucormycosis (ROM) is a life-threatening, fungal infection, primarily affecting immunocompromised patients. The role of orbital exenteration in treatment remains debated, especially regarding its impact on survival outcomes. This case series presents two patients from our Ophthalmology department and compares them with eight cases from the literature, focusing on treatment outcomes and survival rates. We specifically explore the impact of orbital exenteration and other management strategies. The analysis reveals that survival outcomes are closely linked to the timely initiation of antifungal therapy, the patient's underlying conditions, and the extent of orbital involvement at the time of diagnosis. Our findings, in line with the literature, show that early-stage ROM can be treated successfully with less invasive methods, while advanced cases may require orbital exenteration. The need for exenteration should be evaluated on a case-by-case basis, with early detection and appropriate antifungal treatment being critical factors for survival. This study highlights the importance of early diagnosis and individualized treatment plans, emphasizing that while orbital exenteration may improve survival in severe cases, less invasive interventions should be considered for less advanced ROM. Further research and standardized guidelines are needed to refine treatment strategies.
Keywords: Mucorales; ORBITAL exenteration; orbital apex syndrome; rhino-orbital mucormycosis; surgical debridement.
© 2025 Boqaaiya et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Survival benefit of exenteration in COVID-19-associated rhino-orbital mucormycosis.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2024 Feb 1;72(2):190-194. doi: 10.4103/IJO.IJO_2543_22. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38099361 Free PMC article.
-
EORTC guidelines for the use of erythropoietic proteins in anaemic patients with cancer: 2006 update.Eur J Cancer. 2007 Jan;43(2):258-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2006.10.014. Epub 2006 Dec 19. Eur J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17182241
-
Surgical orbital decompression for thyroid eye disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Dec 7;(12):CD007630. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007630.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 22161415
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Topotecan, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride and paclitaxel for second-line or subsequent treatment of advanced ovarian cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Mar;10(9):1-132. iii-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta10090. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16545208
References
-
- Pfaffenbach B, Donhuijsen K, Pahnke J, et al. Systemische Pilzinfektionen bei hamatologischen Neoplasien. Eine Autopsiestudie an 1053 Patienten. Medizinische Klinik. 1994;89(6):299–304. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

