Transdermal microneedle integrating a biomimetic self-enhancing Fenton reaction nano-reactor for alleviating rheumatoid arthritis by inflammatory microenvironment remodeling
- PMID: 40585995
- PMCID: PMC12204083
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.114855
Transdermal microneedle integrating a biomimetic self-enhancing Fenton reaction nano-reactor for alleviating rheumatoid arthritis by inflammatory microenvironment remodeling
Abstract
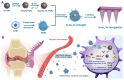
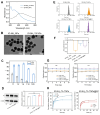
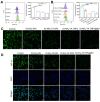
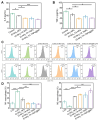
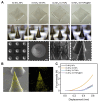
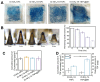
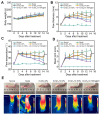
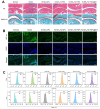
Rationale: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune inflammatory disease, and persistent inflammation in multiple joints is an important sign for the progression of RA. To this end, we developed the transdermal microneedle integrating biomimetic self-enhancing Fenton reaction nano-reactor, for the purposes of eliminating reactive oxygen species, reducing hypoxia and inflammation, and regulating macrophage phenotype. Methods: A novel biomimetic self-enhanced Fenton reaction nano-reactor was synthesized using an M1 macrophage cell membrane-coated tannic acid-modified iron oxide nanoparticle (IO-NH2-TA TNPs@M1). The regulatory mechanisms of the IO-NH2-TA TNPs@M1 were investigated by evaluating ROS scavenging, degree of hypoxia, adsorption of pro-inflammatory factors, and M2 macrophage polarization. Then, the nano-reactor was incorporated into a dissolving microneedle, utilizing enzyme-cut oligomeric sodium hyaluronate, and subsequently assessed for pharmacodynamics and safety. Results: In vitro mechanisms of IO-NH2-TA TNPs@M1 included eliminating ROS, inhibiting the expression of HIF-1α, decreasing the content of pro-inflammatory factors (IL-6 and TNF-α), and inducing macrophage M2 polarization. Pharmacodynamic and in vitro mechanistic studies showed that IO-NH2-TA TNPs@M1DM maximally alleviated joint swelling and fever, protected joint cartilage, improved the local hypoxia environment and promoted macrophage M2 polarization. Cytotoxicity assays and HE staining showed that IO-NH2-TA TNPs@M1DM displayed good biocompatibility. Conclusions: This study designed and synthesized an innovative biomimetic self-enhancing Fenton reaction nano-reactor, and utilized microneedles for the transdermal delivery, providing a scientific and effective new strategy for the precise treatment of RA.
Keywords: M2 macrophage polarization; ROS scavenging; inflammation; reducing hypoxia.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
DS-Modified Paeoniflorin pH-Responsive Lipid-Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles for Targeted Macrophage Polarization in a Rat Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jul 12;20:8967-8992. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S516434. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40671689 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Protein Diet Inhibits the Synovial Tissue Macrophage Pro-Inflammatory Polarization Via NRF2/SIRT3/SOD2/ROS Pathway in K/BxN Rheumatoid Arthritis Mice.Inflammation. 2025 Aug;48(4):1689-1703. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02145-9. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 39292325
-
Engineered Panax notoginseng polysaccharide micelles inhibit macrophage polarization and delay the progression of rheumatoid arthritis via JAK2-STAT3 signaling pathway.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Jul 14;23(1):509. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03576-8. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40660236 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults and an economic evaluation of their cost-effectiveness.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Nov;10(42):iii-iv, xi-xiii, 1-229. doi: 10.3310/hta10420. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 17049139
-
Role of the intestinal flora-immunity axis in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis-mechanisms regulating short-chain fatty acids and Th17/Treg homeostasis.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jun 21;52(1):617. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10714-w. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40544212 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

