Connecting tubules: mechanisms of endoplasmic reticulum membrane fusion
- PMID: 40587263
- PMCID: PMC12312388
- DOI: 10.1042/BST20253043
Connecting tubules: mechanisms of endoplasmic reticulum membrane fusion
Abstract
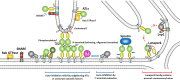
Atlastins (ATLs) are integral dynamin-like GTPases that are critical for the formation and maintenance of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) network, one of the most complex and essential organelles in eukaryotic cells. The ER, which is composed of interconnected tubules and sheets, serves vital functions, including calcium storage, protein and lipid synthesis, and inter-organelle communication. Homotypic membrane fusion, mediated by ATLs, ensures the tubular structure of the ER by generating and stabilizing three-way junctions. Humans express three ATL paralogs, called ATL1, ATL2, and ATL3, which have distinct expression patterns and regulatory mechanisms. Mutations in these proteins are linked to hereditary sensory neuropathies and hereditary spastic paraplegia, highlighting their critical importance in cellular and neuronal health. Here, we review recent studies providing insights into how ATLs are regulated by their N- and C-terminal extensions, as well as how extrinsic factors potentially regulate the activities of ATLs to establish and maintain the normal ER structure.
Keywords: GTPases; endoplasmic reticulum; membrane fusion; organelle biogenesis.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

