Process evaluation of a pragmatic, multicentre pilot Randomised Controlled Trial (RCT) in primary care: Tailored intervention for COPD and Co-morbidities by Pharmacists and Consultant Physicians (TICC PCP)
- PMID: 40587568
- PMCID: PMC12208426
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0326178
Process evaluation of a pragmatic, multicentre pilot Randomised Controlled Trial (RCT) in primary care: Tailored intervention for COPD and Co-morbidities by Pharmacists and Consultant Physicians (TICC PCP)
Abstract
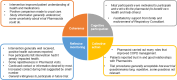
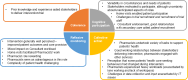
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a growing global challenge. We undertook a process evaluation embedded within the Tailored Intervention at home for patients with moderate-to-severe COPD and Co-Morbidities by Pharmacists and Consultant Physicians (TICC PCP) pilot randomised controlled trial (RCT), which explored patient/stakeholder perceptions of the intervention, acceptability of trial procedures, and barriers/facilitators to intervention implementation. Semi-structured telephone interviews were conducted with intervention patients (20) and stakeholders (10); data were analysed thematically, conceptualised through Normalisation Process Theory. Patient perspectives compared based on socio-economic status (SES). Patients/stakeholders reported positive perceptions of the intervention/trial procedures. Pharmacists provided support across a range of health/social issues. Challenges related to: recruitment; workload/lone-working; managing patient complexity; and data collection. There were suggestions Pharmacists were able to undertake more actions to support patients from low SES areas. Overall, intervention and trial procedures were acceptable to patients and stakeholders. Findings support progression to full-scale RCT.
Copyright: © 2025 Wood et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- The Scottish Government. COPD Best Practice Guide The Scottish Government; 2017.
-
- Vos T, Lim SS, Abbafati C, Abbas KM, Abbasi M, Abbasifard M, et al. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2020;396(10258):1204–22. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30925-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Snell N, Strachan D, Hubbard R, Gibson J, Gruffydd-Jones K, Jarrold I. S32 Epidemiology of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in the uk: findings from the british lung foundation’s ‘respiratory health of the nation’ project. Thorax. 2016;71(Suppl 3):A20.1-A20. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2016-209333.38 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

