Signaling pathways and targeted therapy for pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 40588471
- PMCID: PMC12209467
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-025-02287-8
Signaling pathways and targeted therapy for pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
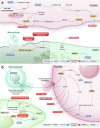
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a global health issue characterized by high mortality. The main targets for current therapies in PH focus on the prostacyclin, nitric oxide, and endothelin pathways. While the approaches targeting these pathways form the foundation of standard PH treatment, the challenge remains to develop more effective therapeutic strategies. Evidence of pathological characteristics in PH illustrates other cell signaling pathways that also participate in the proliferation, apoptosis, extracellular matrix remodeling, mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation, endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition, ferroptosis, pyroptosis, and the intricate network of cell-cell interactions of endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, fibroblasts, and macrophages. In this review, we explore the roles of twenty key signaling pathways in PH pathogenesis. Furthermore, the crosstalks among some pathways offer a more detailed understanding of the complex mechanisms of PH. Considering the crucial role of signaling pathways in PH progression, targeting these aberrant signaling or their hub molecules offers great potential for mitigating PH pathology. This review delves into a variety of therapeutic approaches for PH that target critical signaling pathways and network interactions, including gene therapy, cell therapy, and pharmacological interventions. Supported by evidence from both animal studies and clinical trials, these strategies aim to reverse pathological alterations in pulmonary vessels and restore their normal function, addressing the significant health challenges associated with PH.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
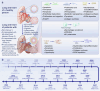
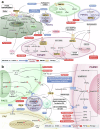
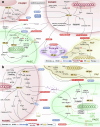

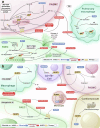



References
-
- Ruopp, N. F. & Cockrill, B. A. Diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: a review. JAMA327, 1379–1391 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Humbert, M. et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Heart J.43, 3618–3731 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Cahal, D. A. Appetite suppressants and pulmonary hypertension. Lancet1, 947 (1969). - PubMed
-
- Mocumbi, A. et al. Pulmonary hypertension. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim.10, 1 (2024). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 81700055/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81930012/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81930012, 81730013, 81720108003, and 82130015/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82130002/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

