Chemosensor receptors are lipid-detecting regulators of macrophage function in cancer
- PMID: 40588561
- PMCID: PMC12208882
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-025-02191-x
Chemosensor receptors are lipid-detecting regulators of macrophage function in cancer
Abstract
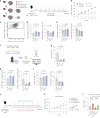
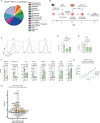
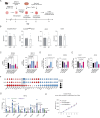
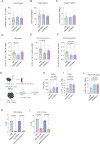
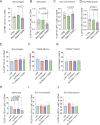
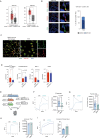
Infiltration of macrophages into tumors is a hallmark of cancer progression, and re-educating tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) toward an antitumor status is a promising immunotherapy strategy. However, the mechanisms through which cancer cells affect macrophage education are unclear, limiting the therapeutic potential of this approach. Here we conducted an unbiased genome-wide CRISPR screen of primary macrophages. Our study confirms the function of known regulators in TAM responses and reveals new insights into the behavior of these cells. We identify olfactory and vomeronasal receptors, or chemosensors, as important drivers of a tumor-supportive macrophage phenotype across multiple cancers. In vivo deletion of selected chemosensors in TAMs resulted in cancer regression and increased infiltration of tumor-reactive CD8+ T cells. In human prostate cancer tissues, palmitic acid bound to olfactory receptor 51E2 (OR51E2) expressed by TAMs, enhancing their protumor phenotype. Spatial lipidomics analysis further confirmed the presence of palmitic acid in close proximity to TAMs in prostate cancer, supporting the function of this lipid mediator in the tumor microenvironment. Overall, these data implicate chemosensors in macrophage sensing of the lipid-enriched milieu and highlight these receptors as possible therapeutic targets for enhancing antitumor immunity.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: E.L. received research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb unrelated to this study and consulting fees from Swarm Therapeutics, Menarini, Amgen, Pfizer and BioLegend. F.B. has received institutional research funds from ADC Therapeutics, Bayer AG, BeiGene, Floratek Pharma, Helsinn, HTG Molecular Diagnostics, Ideogen AG, Idorsia Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Immagene, ImmunoGen, Menarini Ricerche, Nordic Nanovector ASA, Oncternal Therapeutics and Spexis AG; consultancy fees from BIMINI Biotech, Floratek Pharma, Helsinn, Immagene, Menarini and Vrise Therapeutics; advisory board fees to the institution from Novartis. F.B. has also provided expert statements to HTG Molecular Diagnostics and has received travel grants from Amgen, Astra Zeneca and iOnctura. H.M. has received royalties from Chemcom, research grants from Givaudan and consultant fees from Kao. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures











References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AIRC IG ID-29492/Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (Italian Association for Cancer Research)
- AIRC Bridge ID-27673/Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (Italian Association for Cancer Research)
- AIRC ID-22757/Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (Italian Association for Cancer Research)
- GR-2019-1236851/Ministero della Salute (Ministry of Health, Italy)
- AIRC ID-22588/Fondazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (Italian Foundation for Cancer Research)
- AIRC ID-27391/Fondazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (Italian Foundation for Cancer Research)
- Fellowship to Federica Portale/Fondazione Pezcoller (Pezcoller Foundation)
- INNOVA, project no. PNC-E3-2022-23683266 PNC-HLS-DA/Ministero dell'Istruzione, dell'Università e della Ricerca (Ministry of Education, University and Research)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

