Identification and characterization of novel CRESS-DNA viruses in the human respiratory tract
- PMID: 40588733
- PMCID: PMC12207797
- DOI: 10.1186/s12985-025-02742-6
Identification and characterization of novel CRESS-DNA viruses in the human respiratory tract
Abstract
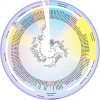
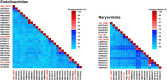
CRESS-DNA viruses are small, circular, single-stranded DNA viruses that have been identified in diverse environments and hosts, including vertebrates, invertebrates, and environmental samples. However, their diversity and role in the human respiratory tract remain poorly understood. In this study, we employed viral metagenomics to analyze 140 nasopharyngeal swab samples from asymptomatic individuals. High-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics analyses were used to identify and characterize novel CRESS-DNA viruses. Phylogenetic relationships were inferred based on Rep protein sequences using maximum likelihood analysis. We identified and characterized eight novel CRESS-DNA viruses, which were classified into the families Endolinaviridae and Naryaviridae, with one potentially representing a novel viral family. These viruses exhibited typical circular genomic structures encoding Rep and Cap proteins, with conserved motifs associated with rolling circle replication. Phylogenetic analysis showed that some viruses were closely related to sequences from vertebrate hosts or environmental samples, suggesting a diverse ecological distribution. Our findings expand the known diversity of CRESS-DNA viruses in the human respiratory tract and highlight their potential ecological and evolutionary significance. Further studies are needed to explore their host specificity, replication mechanisms, and potential roles in human health and disease.
Keywords: Cressdnaviricota; Endolinaviridae; Naryaviridae; Metagenomics; Phylogenetics; Respiratory tract.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

