Establishing a Malonyl-CoA Biosensor for the Two Model Cyanobacteria Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 and Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942
- PMID: 40588753
- PMCID: PMC12281612
- DOI: 10.1021/acssynbio.5c00320
Establishing a Malonyl-CoA Biosensor for the Two Model Cyanobacteria Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 and Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942
Abstract
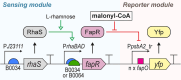
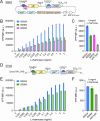
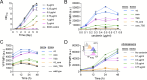
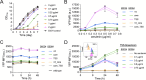
Malonyl-CoA, produced by the first committed step of fatty acid biosynthesis, is a precursor for many valuable bioproducts, making it an important metabolic engineering target. Here, we establish a malonyl-CoA biosensor for the model cyanobacteria Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 and Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942. The developed biosensor utilizes FapR, a malonyl-CoA-regulated transcriptional repressor from Bacillus subtilis, and novel FapR-regulated and cyanobacteria-compatible hybrid promoters for expressing Yfp, the biosensor output reporter. A l-rhamnose-inducible promoter PrhaBAD, characterized in combination with ribosome binding sites of varied strengths, was evaluated for titratable FapR expression. Additionally, the placement and quantity of the FapR-recognized operator within the hybrid promoter was evaluated for its effect on biosensor performance. The optimal operator placement was found to differ for the biosensor variants that achieved maximum reporter expression in the two considered model cyanobacteria. Overall, this biosensor provides new opportunities for further development of cyanobacterial cell factories.
Keywords: biosensor; cyanobacteria; inducible promoter; malonyl-CoA; synthetic biology; transcriptional repressor.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

