CITA GO-ON study. A community based multidomain lifestyle intervention to prevent cognitive decline. Protocol design and recruitment process
- PMID: 40589624
- PMCID: PMC12206835
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1539711
CITA GO-ON study. A community based multidomain lifestyle intervention to prevent cognitive decline. Protocol design and recruitment process
Abstract
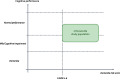
Introduction: Growing research suggests that dementia is a complex disorder with multiple risk factors and causes. The Finnish Geriatric Intervention Study to Prevent Cognitive Impairment and Disability (FINGER) demonstrated that lifestyle interventions could confer cognitive benefits. Inspired by this, the GOIZ-ZAINDU (GZ) feasibility study adapted the FINGER approach to the Basque context. Building upon the GZ study, the CITA GO-ON trial aims to enhance and expand the evidence supporting dementia prevention through a multidomain intervention of risk factor management and resilience promotion.
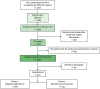
Methods: It is a two-year, population-based, randomized controlled trial to prevent cognitive decline in adults aged 60-85 years with Cardiovascular Risk Factors, Aging and Dementia (CAIDE) risk score ≥6, no dementia, and below-than-expected performance on at least one of three cognitive screening tests. Participants are randomized (1:1) to receive either Regular Health Advice (RHA) or a Multidomain Intervention (MD-Int) that encompasses cognitive training, socio-emotional skills, multicomponent physical exercise, nutritional and culinary intervention, and monitoring for cardiovascular risks, pharmacological drug mismanagement, and comorbidities. The primary outcome is the efficacy of the intervention to reduce the risk of cognitive decline measured by the global composite z-score of the modified Neuropsychological Test Battery over two years. The secondary outcomes measure cost-effectiveness, quality of life, and functional abilities. Blood samples and brain imaging will also be collected to evaluate the effects of the intervention on brain structure and plasma biomarkers.
Results: Recruitment has been completed with 1051 participants selected (mean age (standard deviation, SD) of 69.65 (6.36), 58,50 % female, and mean CAIDE (SD) of 7.62 (1.427). The final participant is expected to complete the last study visit by the autumn of 2026.
Discussion: The CITA GO-ON Study, as a part of the World-Wide FINGERS network, is designed to validate the efficacy of a multidomain lifestyle intervention for dementia prevention and contribute valuable data to inform public health strategies fostering healthy, active aging.
Keywords: cognitive impairment; dementia prevention; lifestyle; multidomain intervention; randomized trial data collection.
Copyright © 2025 Tainta, Ecay-Torres, Barandiaran, Estanga, López, Altuna, Iriondo, Saldias, Garcia-Sebastian, Cañada, de Arriba, Reparaz-Escudero, Sáez de Asteasu, Izquierdo, Balluerka, Gorostiaga, Ros, Soroa, Domper, Gayoso, Arrizabalaga-Lopez, Etxeberria, Torres, Alberdi, Capetillo-Zarate, Mateo-Abad, Vergara, Mar and Martinez-Lage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Andrieu S., Guyonnet S., Coley N., Cantet C., Bonnefoy M., Bordes S., et al. (2017). Effect of long-term omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation with or without multidomain intervention on cognitive function in elderly adults with memory complaints (MAPT): a randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 16, 377–389. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(17)30040-6, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barajas S., Garra L. (2014). Mindfulness and psychopathology: adaptation of the mindful attention awareness scale (MAAS) in a Spanish sample. Clínica Salud 25, 49–56. doi: 10.1016/s1130-5274(14)70026-x, PMID: - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous