Lactylation in tumor: mechanisms and therapeutic potentials
- PMID: 40589733
- PMCID: PMC12206707
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1609596
Lactylation in tumor: mechanisms and therapeutic potentials
Abstract
Lactate, a central product of glucose metabolism, plays a vital role in energy supply and signal transduction, and it also participates in gene transcription regulation through lactylation. Metabolic reprogramming is a key feature of tumor cells and highlights the important role of lactylation in cancer development. Recent studies have emphasized the significant regulatory roles of lactylation in cancer, suggesting that it may serve as a potential target for treatment. This review discusses the mechanisms, regulation, and functions of lactylation in cancer. It also explores the possible significance of lactylation as a marker for the diagnosis and therapy of tumor, and evaluates the therapeutic prospects of targeting lactylation. While the precise mechanisms of lactylation in cancer regulation require further investigation, its significant influence indicates promising avenues for future research.
Keywords: lactate; lactylation; post-translational modifications; tumor metabolism; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Rong, Ma and Peng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
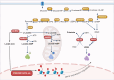
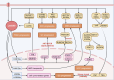
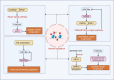
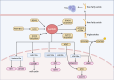
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

